Math Tricks
Introduction
📌 TIPS | HACKS WHICH YOU CAN'T IGNORE AS A CODER ✨🎩 - LeetCode Discuss
Whenever you get an integer conversion problem, think of modulo % and floor division //
6.2 epi
Tips & Tricks
How to multiply matrices
row * col
Examples
-
Integer to Roman


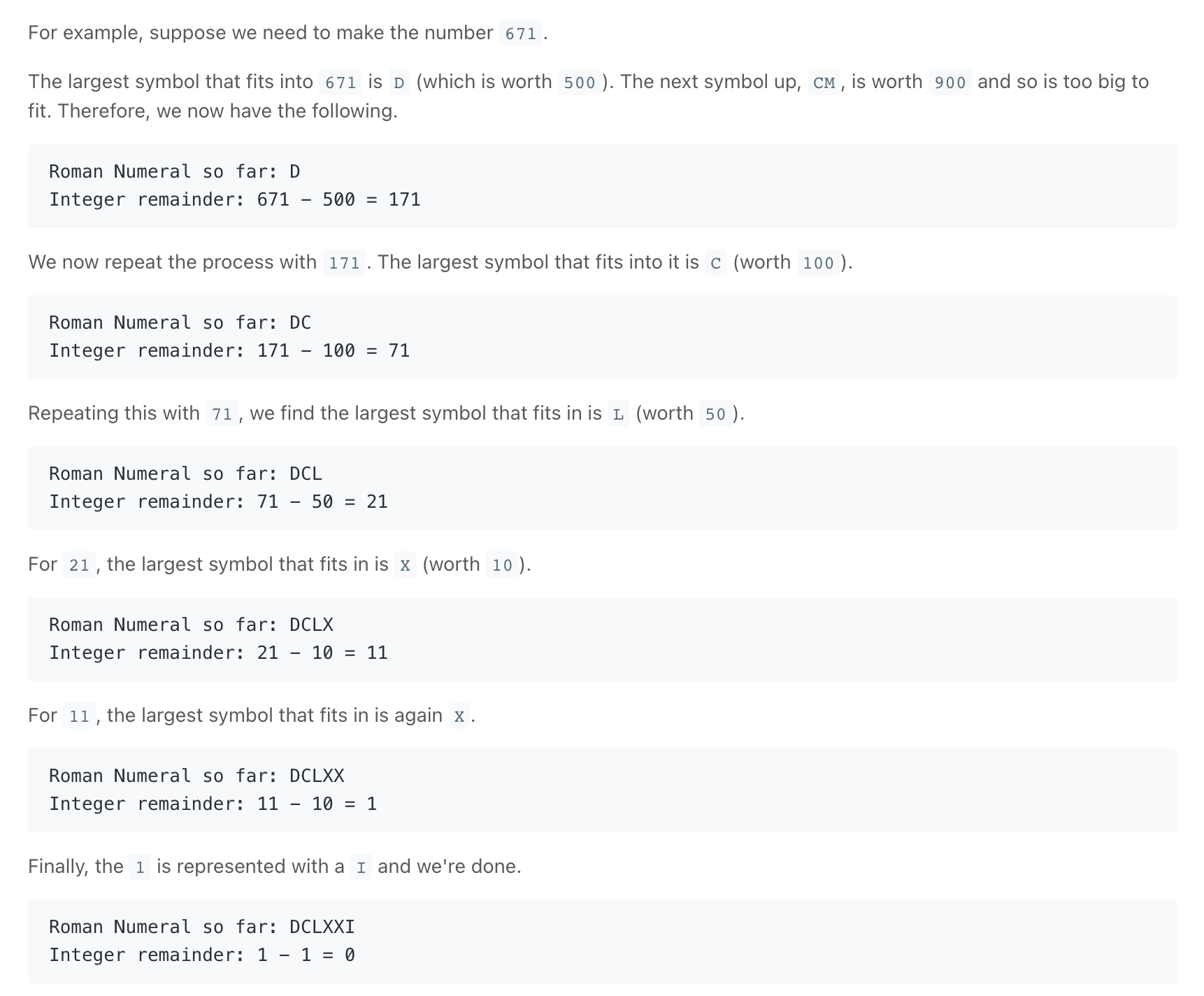
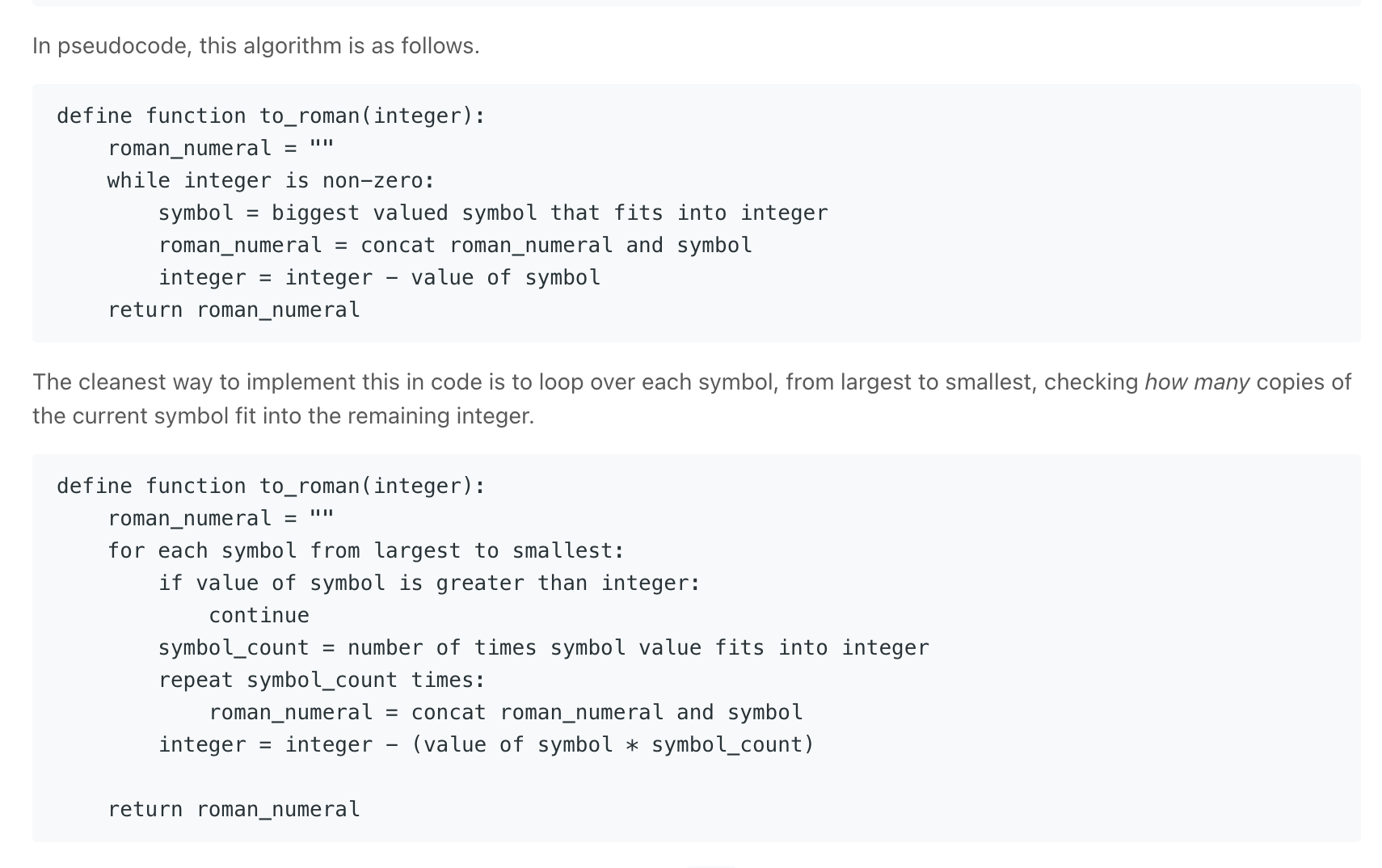
class Solution { private static final int[] values = {1000, 900, 500, 400, 100, 90, 50, 40, 10, 9, 5, 4, 1}; private static final String[] symbols = {"M","CM","D","CD","C","XC","L","XL","X","IX","V","IV","I"}; public String intToRoman(int num) { StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder(); // Loop through each symbol, stopping if num becomes 0. for (int i = 0; i < values.length && num > 0; i++) { // Repeat while the current symbol still fits into num. while (values[i] <= num) { num -= values[i]; sb.append(symbols[i]); } } return sb.toString(); } }class Solution: def intToRoman(self, num: int) -> str: digits = [(1000, "M"), (900, "CM"), (500, "D"), (400, "CD"), (100, "C"), (90, "XC"), (50, "L"), (40, "XL"), (10, "X"), (9, "IX"), (5, "V"), (4, "IV"), (1, "I")] roman_digits = [] # Loop through each symbol. for value, symbol in digits: # We don't want to continue looping if we're done. if num == 0: break count, num = divmod(num, value) # Append "count" copies of "symbol" to roman_digits. roman_digits.append(symbol * count) return "".join(roman_digits) -
Reverse Integer
""" Reverse Integer: Given a 32-bit signed integer, reverse digits of an integer. Assume we are dealing with an environment that could only store integers within the 32-bit signed integer range: [−231, 231 − 1]. For the purpose of this problem, assume that your function returns 0 when the reversed integer overflows. https://leetcode.com/problems/reverse-integer/ """ class Solution: def reverse(self, x): res = 0 num = abs(x) while num > 0: last_digit = num % 10 # get last digit res = (10 * res) + last_digit num //= 10 # remove last digit # confirm 32-bit signed integer if res < -2**31 or res > 2**31-1: return 0 # if x < 0: return -res return res class SolutionB: def reverse(self, x: int): # check if negative negative = False if x < 0: negative = True num = list(str(x)) rev_num = [] # skip the minus sign(for negative values) length = len(num) maximum = length if negative: maximum = length - 1 # reverse each character i = 0 while i < maximum: rev_num.append(num.pop()) i += 1 # create new integer res = int("".join(rev_num)) if negative: res = -res # confirm 32-bit signed integer if res < -2**31 or res > 2**31-1: return 0 return res -
Valid Number
""" Valid Number A valid number can be split up into these components (in order): A decimal number or an integer. (Optional) An 'e' or 'E', followed by an integer. A decimal number can be split up into these components (in order): (Optional) A sign character (either '+' or '-'). One of the following formats: One or more digits, followed by a dot '.'. One or more digits, followed by a dot '.', followed by one or more digits. A dot '.', followed by one or more digits. An integer can be split up into these components (in order): (Optional) A sign character (either '+' or '-'). One or more digits. For example, all the following are valid numbers: ["2", "0089", "-0.1", "+3.14", "4.", "-.9", "2e10", "-90E3", "3e+7", "+6e-1", "53.5e93", "-123.456e789"], while the following are not valid numbers: ["abc", "1a", "1e", "e3", "99e2.5", "--6", "-+3", "95a54e53"]. Given a string s, return true if s is a valid number. Example 1: Input: s = "0" Output: true Example 2: Input: s = "e" Output: false Example 3: Input: s = "." Output: false Example 4: Input: s = ".1" Output: true https://leetcode.com/problems/valid-number """ from collections import Counter # O(N) time | O(N) space class Solution: def isNumber(self, s: str): """ - verify all characters are 0-9,e,E,+,-,. - if has e/E's: - run the verifyNumberWithEs(s) - else: - run the verifyNumberWithoutEs(s) """ if not s: return False # verify all characters are 0-9,e,E,+,-,. for char in s: if not (char.isnumeric() or char in "eE+-."): return False # if has e/E's if 'e' in s or 'E' in s: return self.verifyNumberWithEs(s) else: return self.verifyNumberWithoutEs(s) def verifyNumberWithEs(self, s): """ - verify e/E's - only one - split s by the E's - followed by integer (not float) - order: [number, e, number] - run the verifyNumberWithoutEs() on the numbers """ # only one E char_count = Counter(s) if char_count['e'] + char_count['E'] != 1: return False # split s e_split = [] if 'e' in char_count: e_split = s.split("e") else: e_split = s.split("E") if len(e_split) != 2: return False # followed by integer (not float) if "." in e_split[1]: return False # run the verifyNumberWithoutEs() on the numbers return self.verifyNumberWithoutEs(e_split[0]) and self.verifyNumberWithoutEs(e_split[1]) def verifyNumberWithoutEs(self, s): """ Checks if a number is valid without considering e/E's - has numeric characters - check if has zero or one of -,+ at the beginning and remove it - check if has zero or one of . - verify . has digits on either side """ char_count = Counter(s) # has numeric characters if not self.has_numeric_chars(s): return False # check if has zero or one of -,+ at the beginning and remove it sign_count = char_count['+'] + char_count['-'] if not (sign_count == 1 or sign_count == 0): return False s_wo_signs = s if sign_count: s_wo_signs = s[1:] if not self.has_numeric_chars(s_wo_signs): return False if '+' in s_wo_signs or '-' in s_wo_signs: return False # check if has zero or one of . if not (char_count['.'] == 1 or char_count['.'] == 0): return False # verify . has digits on either side dot_split = s_wo_signs.split('.') if not self.has_numeric_chars(dot_split[0]) and not self.has_numeric_chars(dot_split[1]): return False return True def has_numeric_chars(self, s): for char in s: if char.isnumeric(): return True return False """ Constant space """ # O(N) time | O(1) space class Solution_: def isNumber(self, s: str): """ Digits - must exist Signs - one on either side of exponent - at beginning of string or just after exponent - must have digits after it Exponents - must have digits b4 & after it - can only be one Dots - cannot be after exponent - can be only on left side of exponent - max of one - digit on either side Anything else - invalid input """ seen_digit = False seen_exponent = False seen_dot = False for idx, char in enumerate(s): # 0-9 if char.isnumeric(): seen_digit = True # "+-" one on either side of exponent # can be at beginning of string or just after exponent & must have digits after it elif char in "+-": if not (idx == 0 or s[idx-1] in "eE") or idx == len(s)-1: return False # "eE" - must have digits b4 & after it & can only be one elif char in "eE": if not seen_digit or seen_exponent or idx == len(s)-1: return False seen_exponent = True # "." max of one & can be only on left side of exponent & digit on either side elif char == ".": # max of one & can be only on left side of exponent if seen_dot or seen_exponent: return False # digit on either side has_left_digit = False has_right_digit = False if idx > 0 and s[idx-1].isnumeric(): has_left_digit = True if idx < len(s)-1 and s[idx+1].isnumeric(): has_right_digit = True if not (has_left_digit or has_right_digit): return False seen_dot = True # invalid character else: return False # digits must exist return seen_digit """ test cases: "2" "0089" "-0.1" "+3.14" "4." "-.9" "2e10" "-90E3" "3e+7" "+6e-1" "53.5e93" "-123.456e789" "abc" "1a" "1e" "e3" "99e2.5" "--6" "-+3" "95a54e53" """ -
Maximum Swap
""" 670. Maximum Swap: You are given an integer num. You can swap two digits at most once to get the maximum valued number. Return the maximum valued number you can get. Example 1: Input: num = 2736 Output: 7236 Explanation: Swap the number 2 and the number 7. Example 2: Input: num = 9973 Output: 9973 Explanation: No swap. Needs many examples to understand Drawing a chart of heaps and valleys can make it a bit easier to understand 4123 => 4321 4312 => 4321 4321 => 4321 98368 => 98863 1993 => 9913 https://leetcode.com/problems/maximum-swap similar to https://leetcode.com/problems/next-permutation/ """ # use two pointers class Solution_: def maximumSwap(self, num: int): """ Ensure the largest value is as left as possible """ num_arr = list(str(num)) for i in range(len(num_arr)): # find largest that is as right as possible: eg 1993 => 9913 largest = i for idx in range(i+1, len(num_arr)): if int(num_arr[idx]) >= int(num_arr[largest]): largest = idx # if we found a larger value, swap & return if int(num_arr[largest]) > int(num_arr[i]): num_arr[largest], num_arr[i] = num_arr[i], num_arr[largest] return int("".join(num_arr)) return num """ """ class Solution: def maximumSwap(self, num: int): """ Ensure the largest values are as left as possible """ num_arr = list(str(num)) largest_idx_arr = list(range(len(num_arr))) # fill in the largest values to the right for each index in the array largest = len(num_arr)-1 for idx in reversed(range(len(num_arr))): if int(num_arr[idx]) > int(num_arr[largest]): largest = idx largest_idx_arr[idx] = largest # swap left most for idx in range(len(num_arr)): largest_idx = largest_idx_arr[idx] # ignore same size numbers if num_arr[idx] == num_arr[largest_idx]: continue # swap and return num_arr[largest_idx], num_arr[idx] = num_arr[idx], num_arr[largest_idx] return int("".join(num_arr)) return num -
https://leetcode.com/problems/next-greater-element-iii/

-
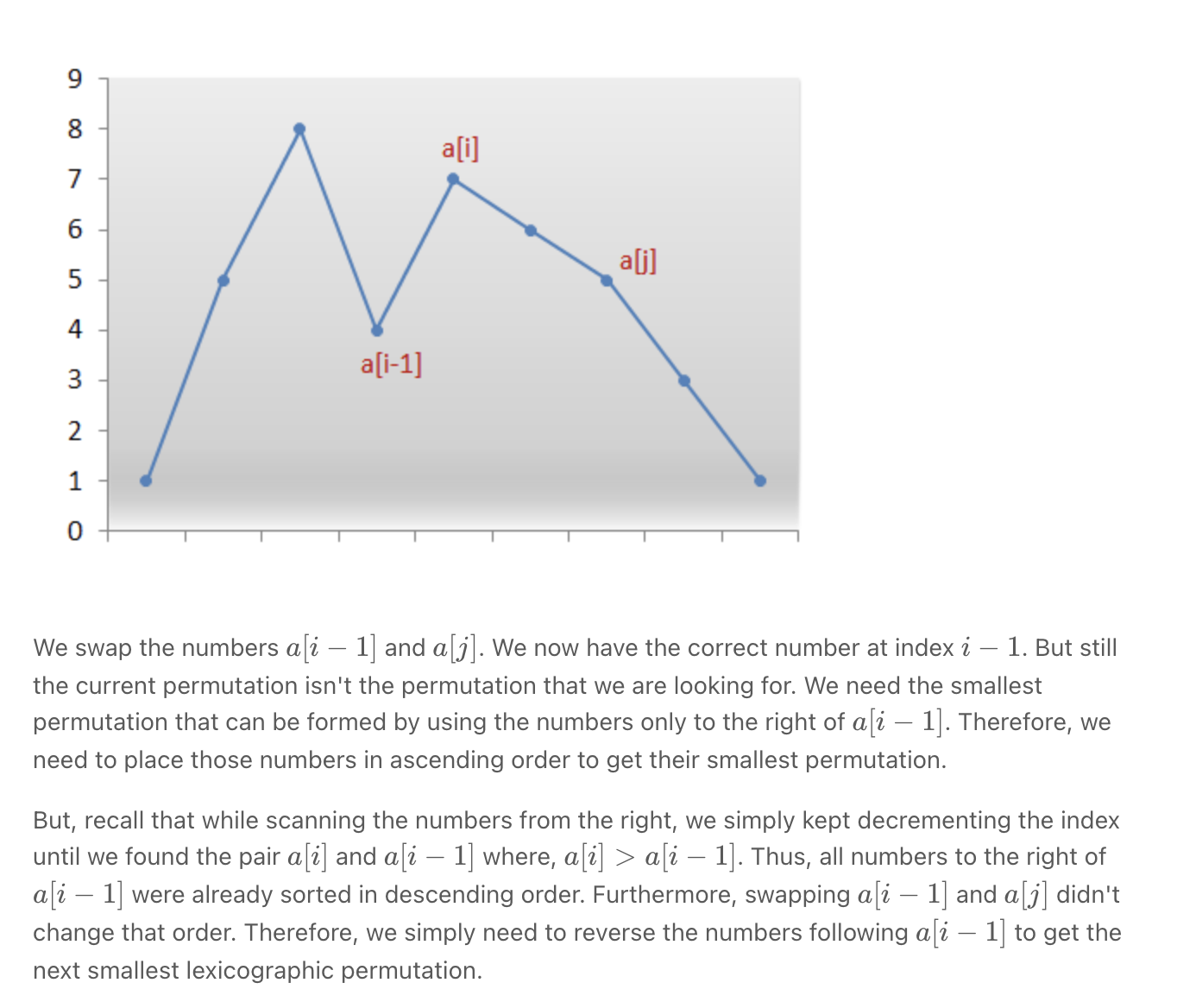
Next Permutation **
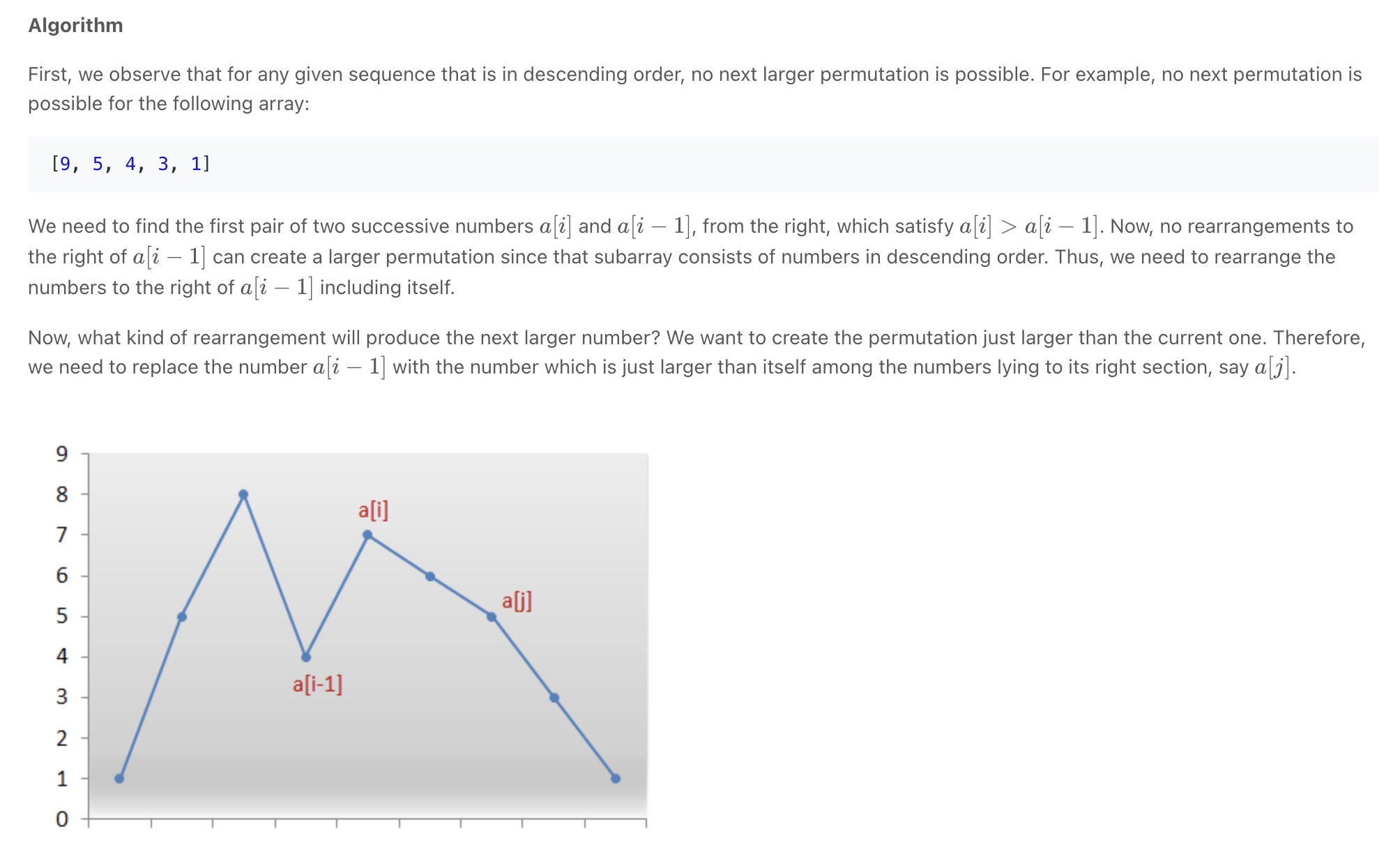


""" Next Permutation: Implement next permutation, which rearranges numbers into the lexicographically next greater permutation of numbers. If such an arrangement is not possible, it must rearrange it as the lowest possible order (i.e., sorted in ascending order). The replacement must be in place and use only constant extra memory. Example 1: Input: nums = [1,2,3] Output: [1,3,2] Example 2: Input: nums = [3,2,1] Output: [1,2,3] Example 3: Input: nums = [1,1,5] Output: [1,5,1] Example 4: Input: nums = [1] Output: [1] Needs many examples to understand Drawing a chart of heaps and valleys can make it a bit easier to understand [1,3,2] => [2,1,3] [1,2,3,4] => [1,2,4,3] [4,1,2,3] => [4,1,3,2] [3,4,2,1] => [4,1,2,3] - swapped 3 & 4 then sorted the numbers to the right of 4 [2,3,4,1] => [2,4,1,3] - swapped 3 & 4 then sorted the numbers to the right of 4 [15,2,--4--,6,--5--,2] => [15,2,--5--,2,4,6] - swapped 4 & 5 then sorted the numbers to the right of 5 https://leetcode.com/problems/next-permutation/ https://www.notion.so/paulonteri/Math-Tricks-8c99fd21a1d343f7bee1eaf0467ea362#4bda6bec59634b1ebf5bc34fb2edc542 similar to https://leetcode.com/problems/maximum-swap """ class Solution: def nextPermutation(self, nums): """ 1. look for peak that has its larger & smaller number furthest to the right - Note: peak => num[right] > num[left] - find **first smaller number** (furthest to the right) - then **find the number furthest to the right that is larger than it** - swap the smaller and larger 2. if no peak was found srt the whole array and return 3. sort the array to the right of where the larger number was placed """ small_num_idx = None # find first smaller number (furthest to the right) i = len(nums)-1 largest = nums[-1] while not small_num_idx and i >= 0: if nums[i] < largest: small_num_idx = i largest = max(largest, nums[i]) i -= 1 # array is sorted in descending order if small_num_idx is None: nums.sort() return # find number (furthest to the right) larger than small_num for idx in reversed(range(small_num_idx+1, len(nums))): if nums[idx] > nums[small_num_idx]: # swap larger and smaller number nums[small_num_idx], nums[idx] = nums[idx], nums[small_num_idx] # sort area after where the larger swapped number was placed self.sort(nums, small_num_idx+1) return def sort(self, nums, sort_start): # nums[sort_start:] = list(sorted(nums[sort_start:])) for idx in range(sort_start, len(nums)): smallest = idx for i in range(idx, len(nums)): if nums[i] < nums[smallest]: smallest = i nums[smallest], nums[idx] = nums[idx], nums[smallest] -
String to Integer & Integer to String
""" Integer to String """ def single_digit_to_char(digit): return chr(ord('0')+digit) def int_to_string(x: int): if x == 0: return "0" is_neg = False if x < 0: is_neg, x = True, -x result = [] while x > 0: digit = x % 10 result.append(single_digit_to_char(digit)) x = x // 10 if is_neg: result.append('-') return "".join(reversed(result)) """ String to Integer """ def single_char_to_int(character): # num_mapping = { # "1": 1, # "2": 2, # "3": 3, # "4": 4, # "5": 5, # "6": 6, # "7": 7, # "8": 8, # "9": 9, # "0": 0, # } # return num_mapping[character] return ord(character) - ord('0') def string_to_int(s: str): is_neg = False num = 0 multiplier = 1 start_idx = 0 if s and s[0] == "-": is_neg, start_idx = True, 1 if s and s[0] == "+": start_idx = 1 for idx in reversed(range(start_idx, len(s))): num += single_char_to_int(s[idx])*multiplier multiplier *= 10 if is_neg: return -num return num print(string_to_int("22"), type(string_to_int("22"))) -
String to Integer (atoi)
""" String to Integer (atoi): Implement atoi which converts a string to an integer. The function first discards as many whitespace characters as necessary until the first non-whitespace character is found. Then, starting from this character takes an optional initial plus or minus sign followed by as many numerical digits as possible, and interprets them as a numerical value. The string can contain additional characters after those that form the integral number, which are ignored and have no effect on the behavior of this function. If the first sequence of non-whitespace characters in str is not a valid integral number, or if no such sequence exists because either str is empty or it contains only whitespace characters, no conversion is performed. If no valid conversion could be performed, a zero value is returned. Only the space character ' ' is considered a whitespace character. Assume we are dealing with an environment that could only store integers within the 32-bit signed integer range: [−231, 231 − 1]. If the numerical value is out of the range of representable values, 231 − 1 or −231 is returned. https://leetcode.com/problems/string-to-integer-atoi/ """ class Solution: def myAtoi(self, string: str): idx = 0 # skip whitespace while idx < len(string) and string[idx] == ' ': idx += 1 # deal with number if idx < len(string) and (string[idx] == '-' or string[idx] == '+' or string[idx].isnumeric()): # find number start = idx if string[idx] == '-' or string[idx] == '+': # handle stuff like "+-12" idx += 1 while idx < len(string) and string[idx].isnumeric(): idx += 1 # convert into number if string[start] == '-': if idx-start == 1: return 0 return -self.convertToIntNeg(string[start+1:idx]) elif string[start] == '+': if idx-start == 1: return 0 return self.convertToIntPos(string[start+1:idx]) return self.convertToIntPos(string[start:idx]) return 0 def convertToIntPos(self, string): integer = int(string) if integer >= 2**31: return 2**31 - 1 return integer def convertToIntNeg(self, string): integer = int(string) if integer >= 2**31: return 2**31 return integer """ # Input: valid string # Output: integer # Assumptions: - some strings might start without white space - only ' ' is considered whitespace - some strings will not contain numerical digits after the whitespace - ignore everythong after the whitespace thet is not a -, + , or a numerical value - return 0 if no valis sol is found # Examples: ' -502apple' -> -502 ' -502 apple' -> -502 ' -502 200' -> -502 '+502 200' -> 502 ' t-502apple' -> 0 # # First Approach: - iterate through the string # skip all the whitespace (while loop 1) # check whether next character is -, + or number: (while loop 2) - if not, return 0 - if it is: continue iterating while storing all it's characters in an array ### O(1) time # convert the stored characters into a number and return the number ### O(n) time - convert the array into an string (skipping -, +) then return it or negate and return it # return 0 ## time O(n) | O(n) space - where n is len(string) # # Second Approach: - iterate through the string # skip all the whitespace (while loop 1) # check whether next character is -, + or number: (while loop 2) - if not, return 0 - if it is: continue iterating (keep track of the satrting and ending indices) ### O(1) time # convert the found number string (we can get it using slicing) into a number and return the number ### O(n) time - return it or negate and return it # return 0 ## time O(n) | O(n) space - where n is len(string) def myAtoi(self, s: str): idx = 0 # skip whitespace while idx < len(string) and string[idx] == ' ': idx += 1 # deal with number if idx < len(string) and (string[idx] == '-' or string[idx] == '+' or string[idx].isnumeric()) # find number start = idx while idx < len(string) and (string[idx] == '-' or string[idx] == '+' or string[idx].isnumeric()) idx += 1 # convert into number if string[start] == '-': return -int(string[start+1:idx]) elif string[start] == '-': return int(string[start+1:idx]) return int(string[start:idx]) return 0 """ -
Multiply Strings *
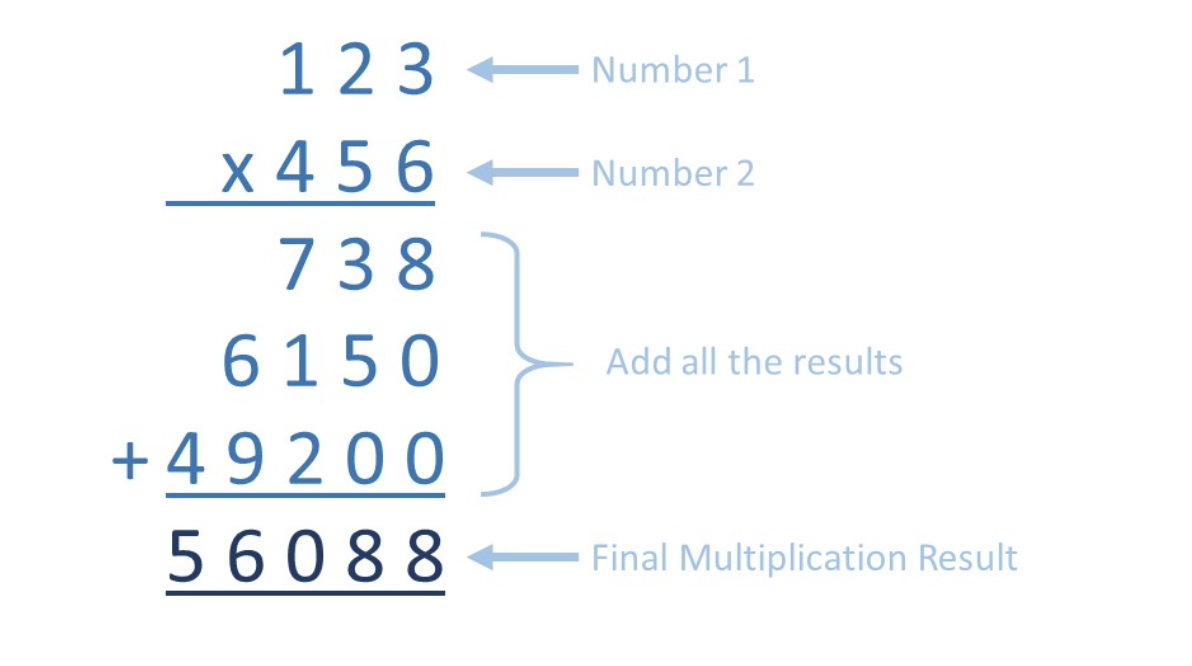


""" Multiply Strings: Given two non-negative integers num1 and num2 represented as strings, return the product of num1 and num2, also represented as a string. Note: You must not use any built-in BigInteger library or convert the inputs to integer directly. Example 1: Input: num1 = "2", num2 = "3" Output: "6" Example 2: Input: num1 = "123", num2 = "456" Output: "56088" https://leetcode.com/problems/multiply-strings """ class Solution: def multiply(self, num1: str, num2: str): if num1 == "0" or num2 == "0": return "0" res = [0] * (len(num1) + len(num2)) for i_one in reversed(range(len(num1))): for i_two in reversed(range(len(num2))): # +1 is used to handle (0,0) i_one=0 i_two=0 carries # placing their carry will be easier if we move every element one step back/ to the right pos = i_one + i_two + 1 carry = res[pos] multiplication = (int(num1[i_one]) * int(num2[i_two])) + carry # save res[pos] = multiplication % 10 # place carry res[pos-1] += multiplication // 10 # remove leading zeros idx = 0 while res[idx] == 0: idx += 1 res = res[idx:] # return answer return "".join([str(num) for num in res]) -
Pascal's Triangle
""" Pascal's Triangle Given an integer numRows, return the first numRows of Pascal's triangle. Example 1: Input: numRows = 5 Output: [[1],[1,1],[1,2,1],[1,3,3,1],[1,4,6,4,1]] Example 2: Input: numRows = 1 Output: [[1]] https://leetcode.com/problems/pascals-triangle """ class Solution: def generate(self, numRows: int): triangle = [] if numRows < 1: return triangle # add the first row triangle.append([1]) for i in range(1, numRows): # start with 2nd row row = [] # we handle the first and last indices separately row.append(1) # first index # items to calculate/add will always be equal to the index (i) - 1 # for example in the 4th row (i=3) we calculate 2 values for x in range(1, i): # we know that each character is the sum of those above it: above left and above right row.append(triangle[i-1][x-1] + triangle[i-1][x]) row.append(1) # last index for row triangle.append(row) return triangle -
Roman to Integer
""" Roman to Integer Roman numerals are represented by seven different symbols: I, V, X, L, C, D and M. Symbol Value I 1 V 5 X 10 L 50 C 100 D 500 M 1000 For example, 2 is written as II in Roman numeral, just two one's added together. 12 is written as XII, which is simply X + II. The number 27 is written as XXVII, which is XX + V + II. Roman numerals are usually written largest to smallest from left to right. However, the numeral for four is not IIII. Instead, the number four is written as IV. Because the one is before the five we subtract it making four. The same principle applies to the number nine, which is written as IX. There are six instances where subtraction is used: I can be placed before V (5) and X (10) to make 4 and 9. X can be placed before L (50) and C (100) to make 40 and 90. C can be placed before D (500) and M (1000) to make 400 and 900. Given a roman numeral, convert it to an integer. Example 1: Input: s = "III" Output: 3 Example 2: Input: s = "IV" Output: 4 Example 3: Input: s = "IX" Output: 9 Example 4: Input: s = "LVIII" Output: 58 Explanation: L = 50, V= 5, III = 3. Example 5: Input: s = "MCMXCIV" Output: 1994 Explanation: M = 1000, CM = 900, XC = 90 and IV = 4. https://leetcode.com/problems/roman-to-integer """ class Solution_: def romanToInt(self, s: str): key_map = { "I": 1, "V": 5, "X": 10, "L": 50, "C": 100, "D": 500, "M": 1000 } num = 0 idx = 0 while idx < len(s): if s[idx] == "I": if idx+1 < len(s) and s[idx+1] == "V": num += 4 idx += 2 elif idx+1 < len(s) and s[idx+1] == "X": num += 9 idx += 2 else: num += key_map[s[idx]] idx += 1 elif s[idx] == "X": if idx+1 < len(s) and s[idx+1] == "L": num += 40 idx += 2 elif idx+1 < len(s) and s[idx+1] == "C": num += 90 idx += 2 else: num += key_map[s[idx]] idx += 1 elif s[idx] == "C": if idx+1 < len(s) and s[idx+1] == "D": num += 400 idx += 2 elif idx+1 < len(s) and s[idx+1] == "M": num += 900 idx += 2 else: num += key_map[s[idx]] idx += 1 else: num += key_map[s[idx]] idx += 1 return num """ """ class Solution: def romanToInt(self, s: str): key_map = { "I": 1, "V": 5, "X": 10, "L": 50, "C": 100, "D": 500, "M": 1000 } num = 0 idx = 0 while idx < len(s): if idx+1 < len(s) and key_map[s[idx]] < key_map[s[idx+1]]: num += key_map[s[idx+1]] - key_map[s[idx]] idx += 2 else: num += key_map[s[idx]] idx += 1 return num -
Basic Calculator II **
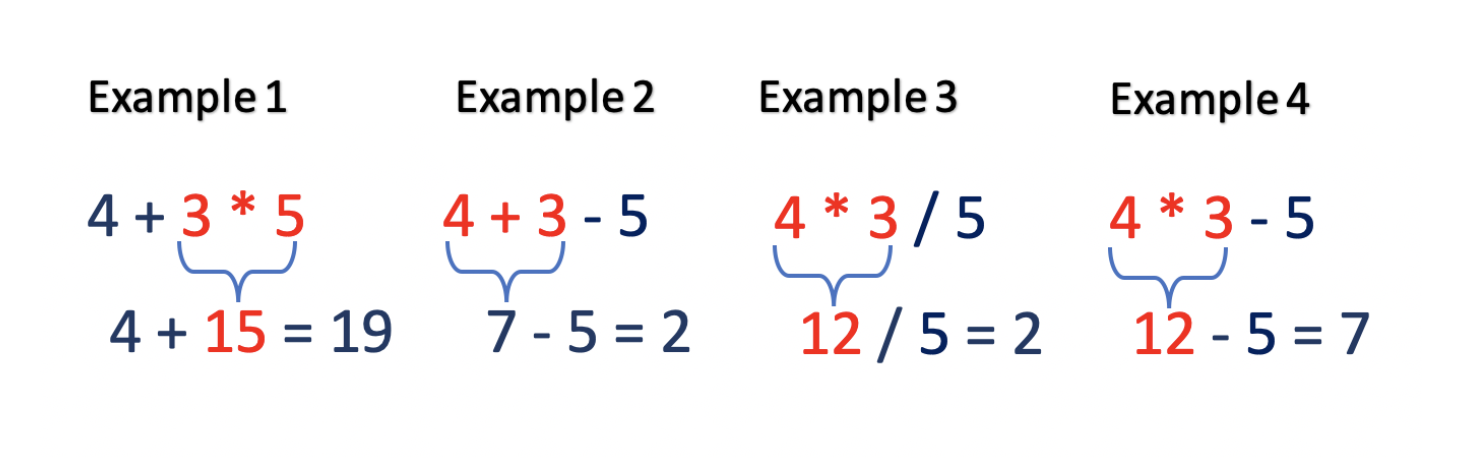
""" Basic Calculator II: Given a string s which represents an expression, evaluate this expression and return its value. The integer division should truncate toward zero. You may assume that the given expression is always valid. All intermediate results will be in the range of [-231, 231 - 1]. Note: You are not allowed to use any built-in function which evaluates strings as mathematical expressions, such as eval(). Example 1: Input: s = "3+2*2" Output: 7 Example 2: Input: s = " 3/2 " Output: 1 Example 3: Input: s = " 3+5 / 2 " Output: 5 https://leetcode.com/problems/basic-calculator-ii/ """ import math """ -------------------------- PROBLEM ---------------------------------- string s which represents an expression, evaluate this expression and return its value not allowed to use any built-in function which evaluates strings as mathematical expressions integer division should truncate toward zero. s represents a valid expression s consists of integers and operators ('+', '-', '*', '/') -------------------------- EXAMPLES ---------------------------------- D/MA/S "1+2" => 3 "3+2*2" => 3+4 = 7 "5/2+3" => 2+3 = 5 "3+5/2" => 3+2 = 5 "3+5/2+5/2" => 3+2+2 = 7 "38765456789+43434345/23434+53434/2" -------------------------- BRUTE FORCE ---------------------------------- O(n^2) time | O(1) time - evaluate each of DMAS and add it back to the string - do division, add it back to the string - multiplication... -------------------------- OPTIMAL ---------------------------------- -------------------------- ONE O(n) time | O(1) time - separate the s into an array that contain intergers and the signs - evaluate each of D/M A/S and add it to an array - do division on array, add the results to after_div array - do multiplication on after_div, add the results to after_mult array - do addition on after_mult... -------------------------- TWO: stack = [0] current_number = "" prev_operand = "+" # deal with * and /: - iterate through the array: - try to build up a number while the characters are numeric - if you get to a sign: - if the prev_operand is * or / : - get the currentNumber and the prevNumber and apply the prev_operand on them then add the result to the stack - if the prev_operand is -: - add neg the number to the stack - if the prev_operand is +: - add the number to the stack - record the new prev_operand - reset current_number = "" - add all the number in the stack """ """ ------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------ """ class Solution1: def calculate(self, s: str): # separate the s into an array that contain integers and the signs arr = [] i = 0 while i < len(s): if s[i].isnumeric(): end = i while end+1 < len(s) and s[end+1].isnumeric(): end += 1 arr.append(int(s[i:end+1])) i = end + 1 elif s[i] == " ": i += 1 else: arr.append(s[i]) i += 1 # division or multiplication after_dm = [] i = 0 while i < len(arr): # check for division if arr[i] == "/": after_dm[-1] = after_dm[-1] // arr[i+1] i += 2 # check for multiplication elif arr[i] == "*": after_dm[-1] = after_dm[-1] * arr[i+1] i += 2 else: after_dm.append(arr[i]) i += 1 # addition or subtraction after_sa = [] i = 0 while i < len(after_dm): # check for subtraction if after_dm[i] == "-": after_sa[-1] = after_sa[-1] - after_dm[i+1] i += 2 # check for addition elif after_dm[i] == "+": after_sa[-1] = after_sa[-1] + after_dm[i+1] i += 2 else: after_sa.append(after_dm[i]) i += 1 return "".join([str(item) for item in after_sa]) """ """ class Solution3: def calculate(self, s: str): # separate the s into an array that contain integers and the signs arr = [] i = 0 while i < len(s): if s[i].isnumeric(): end = i while end+1 < len(s) and s[end+1].isnumeric(): end += 1 arr.append(s[i:end+1]) i = end + 1 elif s[i] == " ": i += 1 else: arr.append(s[i]) i += 1 stack = [] # evaluate addition or subtraction for idx in range(len(arr)): if not arr[idx].isnumeric(): continue current_number = arr[idx] # ignore first number if idx == 0: stack.append(int(current_number)) continue prev_operand = arr[idx-1] if prev_operand == "-": stack.append(-int(current_number)) elif prev_operand == "+": stack.append(int(current_number)) elif prev_operand == "*": prev_num = stack.pop() stack.append(prev_num * int(current_number)) elif prev_operand == "/": prev_num = stack.pop() stack.append(math.trunc(prev_num / int(current_number))) if idx < len(arr): prev_operand = arr[idx] number = 0 while stack: number += stack.pop() return number """ ------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------ """ class Solution2: def calculate(self, s: str): # separate the s into an array that contain integers and the signs arr = [] i = 0 while i < len(s): if s[i].isnumeric(): end = i while end+1 < len(s) and s[end+1].isnumeric(): end += 1 arr.append(s[i:end+1]) i = end + 1 elif s[i] == " ": i += 1 else: arr.append(s[i]) i += 1 stack = [] current_number = "" prev_operand = "+" # evaluate addition or subtraction for idx in range(len(arr)+1): if idx < len(arr) and arr[idx].isnumeric(): current_number = arr[idx] continue if prev_operand == "-": stack.append(-int(current_number)) elif prev_operand == "+": stack.append(int(current_number)) elif prev_operand == "*": prev_num = stack.pop() stack.append(prev_num * int(current_number)) elif prev_operand == "/": prev_num = stack.pop() stack.append(math.trunc(prev_num / int(current_number))) if idx < len(arr): prev_operand = arr[idx] number = 0 while stack: number += stack.pop() return number -
'K' Closest Points to the Origin
-
Angle Between Hands of a Clock
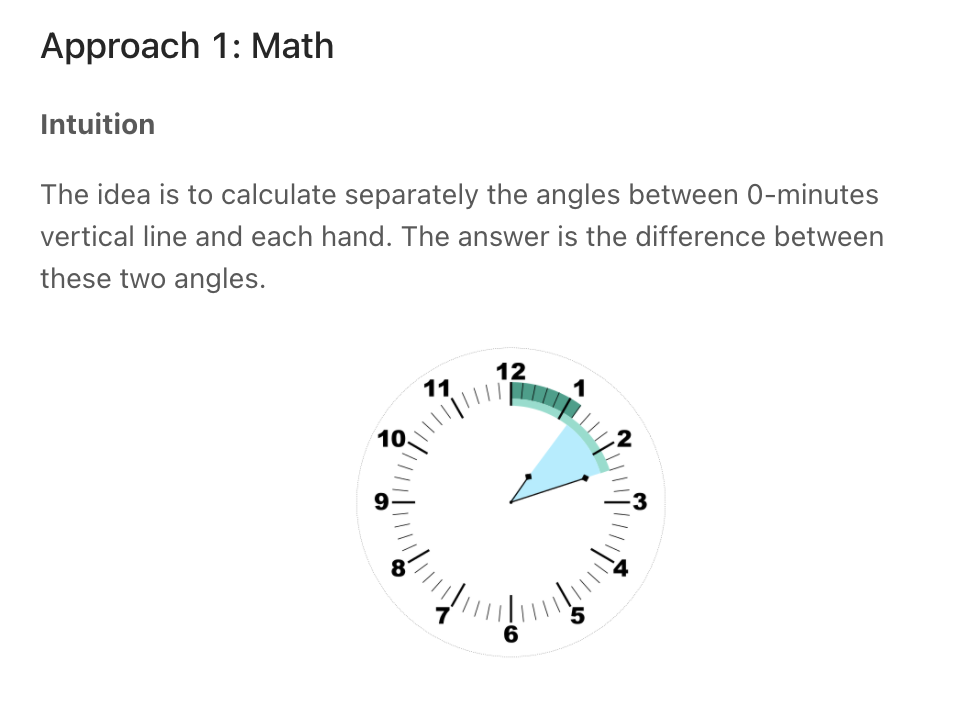
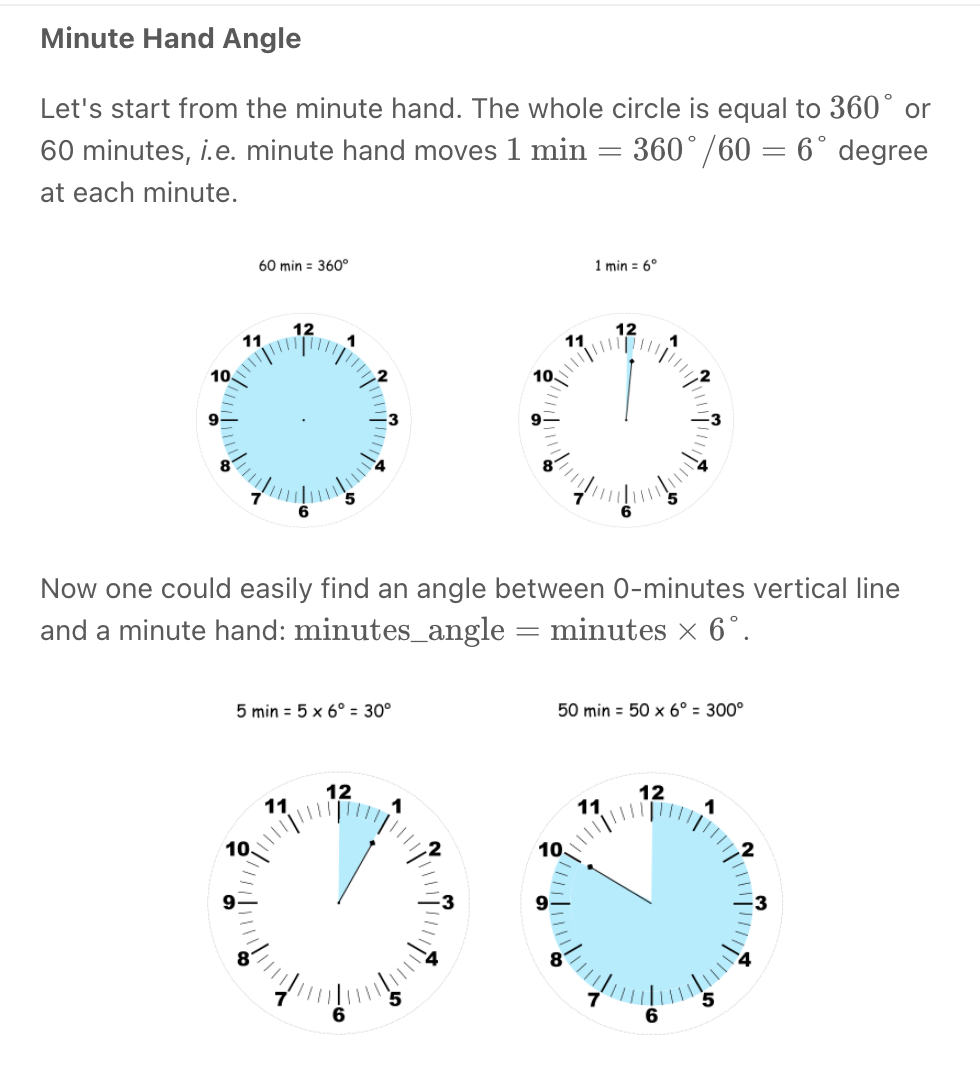
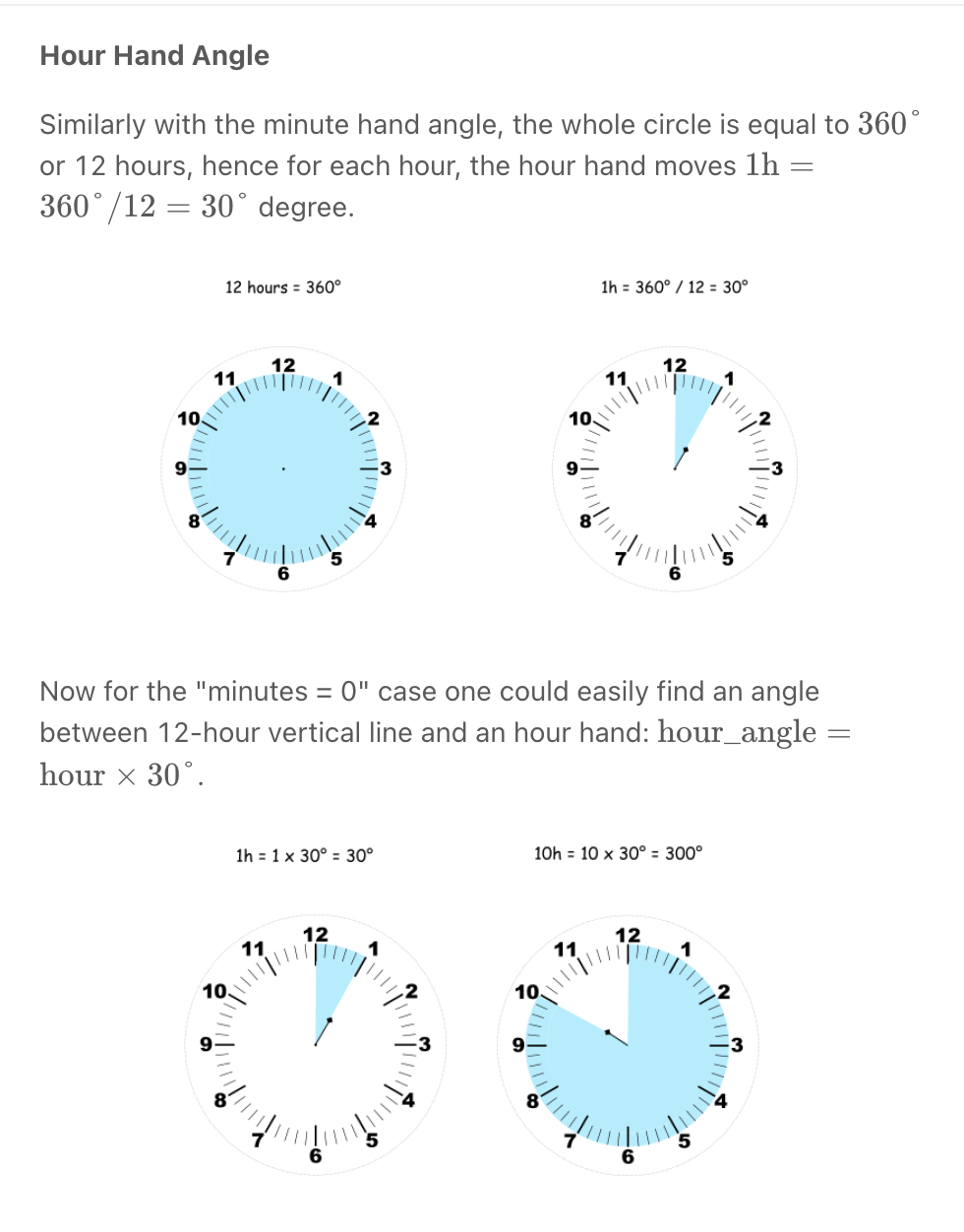
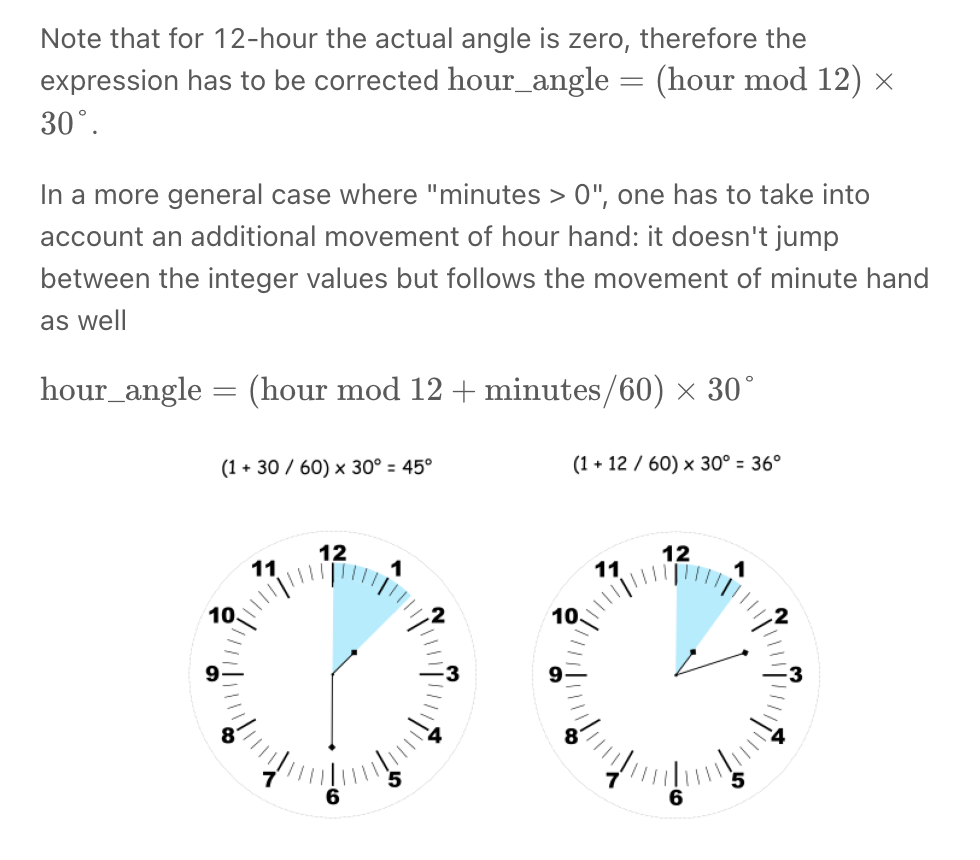
""" Angle Between Hands of a Clock Given two numbers, hour and minutes. Return the smaller angle (in degrees) formed between the hour and the minute hand. Example 1: Input: hour = 12, minutes = 30 Output: 165 Example 2: Input: hour = 3, minutes = 30 Output: 75 Example 3: Input: hour = 3, minutes = 15 Output: 7.5 Example 4: Input: hour = 4, minutes = 50 Output: 155 Example 5: Input: hour = 12, minutes = 0 Output: 0 https://leetcode.com/problems/angle-between-hands-of-a-clock """ class Solution: def angleClock(self, hour: int, minutes: int): """ - calculate hour degree (hour/12 * 360) + (minute/60 * 30) - calculate minute degree - minute/60 * 360 """ hours = hour if hour == 12: hours = 0 hours_degree = (360 * hours/12) + (30 * minutes/60) minutes_degree = 360 * minutes/60 diff = abs(hours_degree-minutes_degree) return min(diff, abs(360-diff)) -
Count Primes *

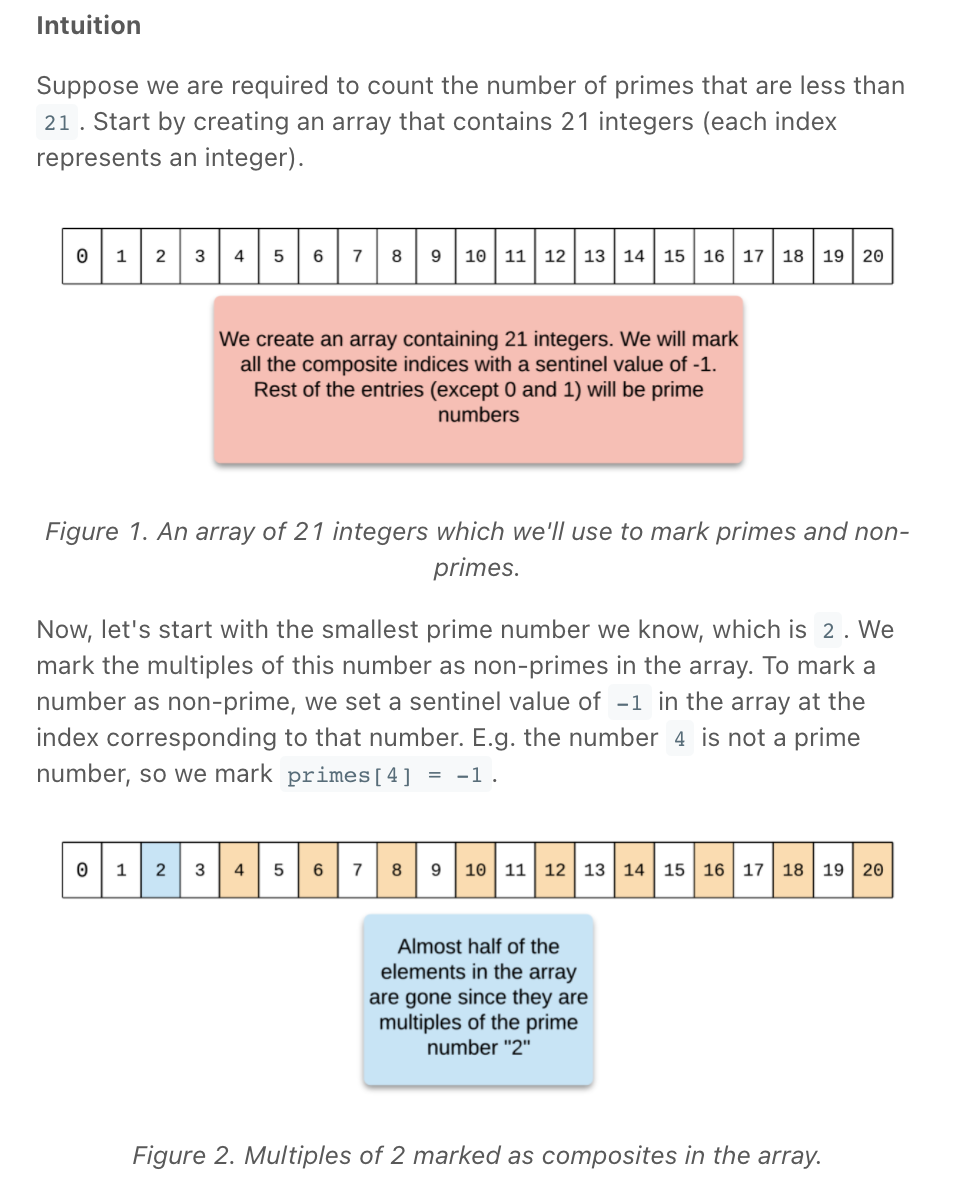
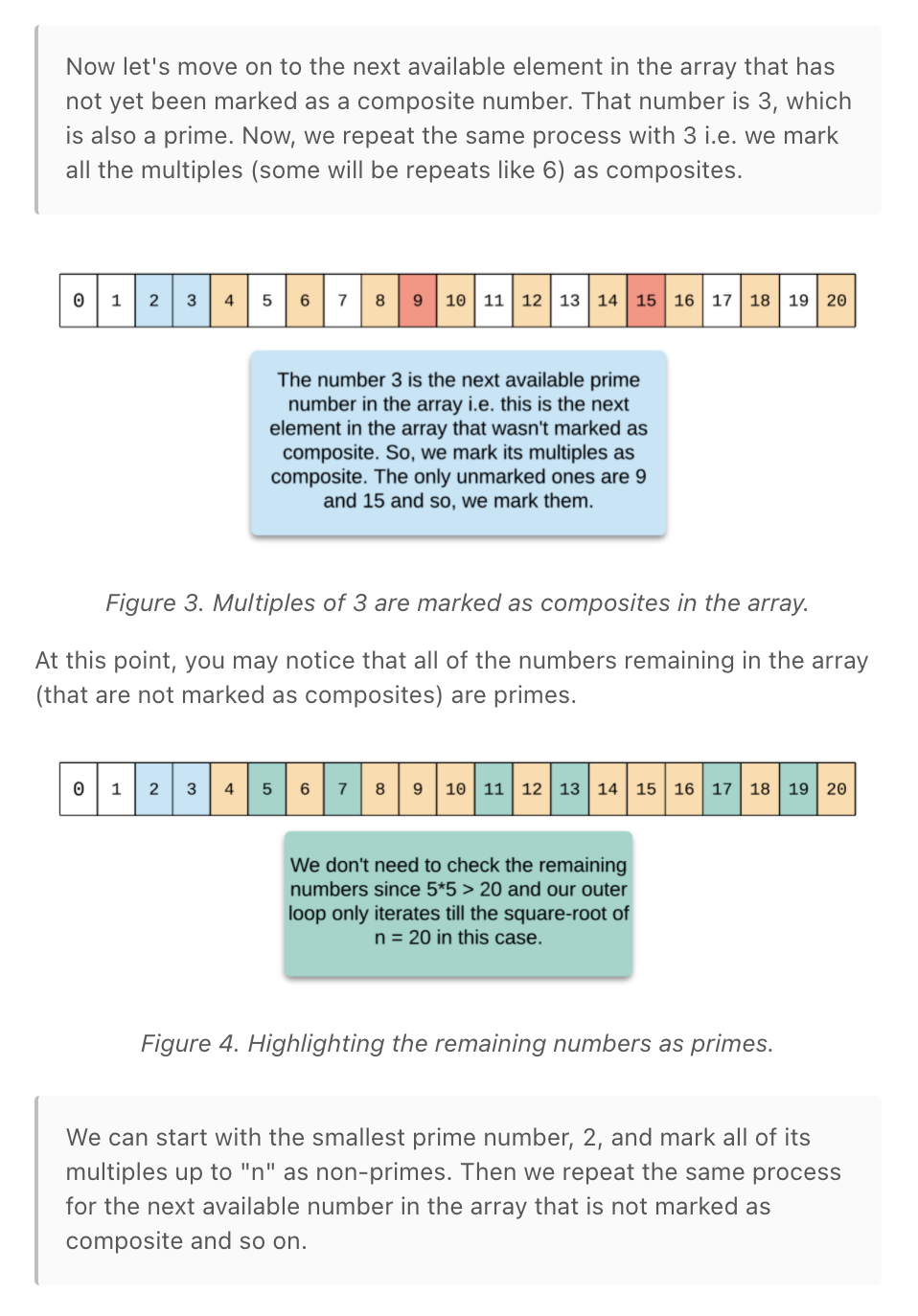



""" Count Primes: Given an integer n, return the number of prime numbers that are strictly less than n. Example 1: Input: n = 10 Output: 4 Explanation: There are 4 prime numbers less than 10, they are 2, 3, 5, 7. Example 2: Input: n = 0 Output: 0 Example 3: Input: n = 1 Output: 0 https://leetcode.com/problems/count-primes """ """ The basic brute-force solution for this problem is to iterate from 0 to n and for each number, we do a prime-check. To check if a number is prime or not, we simply check if its divisors include anything other than 1 and the number itself. If so, then it is not a prime number. This method will not scale for the given limits on n. The iteration itself has O(n) time complexity and for each iteration, we have the prime check which takes O(sqrt)O( n). This will exceed the problem's time limit. Therefore, we need a more efficient solution. Instead of checking if each number is prime or not, what if we mark the multiples of a prime number as non-prime? """ import math class Solution_: # times out on leetcode def isPrime(self, n): for num in range(2, math.floor(math.sqrt(n))): if n % num == 0: return False return True def countPrimes(self, n: int): if n <= 2: return 0 numbers = [-1] * n numbers[0] = False numbers[1] = False for idx in range(2, n): if numbers[idx] == False: continue numbers[idx] = self.isPrime(idx) if numbers[idx]: # only consider primes to ensure not calculating duplicates multiplier = idx while multiplier * idx < n: numbers[multiplier * idx] = False multiplier += 1 return numbers.count(True) """ """ class Solution: def countPrimes(self, n: int): if n <= 2: return 0 numbers = [True] * n numbers[0] = False numbers[1] = False for idx in range(2, n): if numbers[idx]: # only consider primes to ensure not calculating duplicates for multiple in range(idx+idx, n, idx): # start,stop+1,step numbers[multiple] = False return numbers.count(True) -
Robot Bounded In Circle
""" Robot Bounded In Circle: On an infinite plane, a robot initially stands at (0, 0) and faces north. The robot can receive one of three instructions: "G": go straight 1 unit; "L": turn 90 degrees to the left; "R": turn 90 degrees to the right. The robot performs the instructions given in order, and repeats them forever. Return true if and only if there exists a circle in the plane such that the robot never leaves the circle. Example 1: Input: instructions = "GGLLGG" Output: true Explanation: The robot moves from (0,0) to (0,2), turns 180 degrees, and then returns to (0,0). When repeating these instructions, the robot remains in the circle of radius 2 centered at the origin. Example 2: Input: instructions = "GG" Output: false Explanation: The robot moves north indefinitely. Example 3: Input: instructions = "GL" Output: true Explanation: The robot moves from (0, 0) -> (0, 1) -> (-1, 1) -> (-1, 0) -> (0, 0) -> ... https://leetcode.com/problems/robot-bounded-in-circle https://leetcode.com/problems/robot-bounded-in-circle/discuss/290856/JavaC%2B%2BPython-Let-Chopper-Help-Explain """ from enum import Enum """ MOVING: - moving north is adding 1 to y - moving left is adding 1 to x - moving south is subreacting 1 from y - moving left is subreacting 1 from x DIRECTIONS: north west east south SOLUTION: - if we have a loop, because the turnings are of 90 degrees, we should return to 0,0 after running the instructions 4 times if we are done with the instruction once and have changed direction by ((dir) cumulative direction which might be south, east, west) it means that if this (dir) is applied at most 4 times (for east & west (horizontal)) or even 2 times (for north (vertical)) we will be back to the origin """ class Direction(Enum): NORTH = "north" SOUTH = "south" EAST = "east" WEST = "west" class Solution: def isRobotBounded(self, instructions: str): position = [0, 0] direction = Direction.NORTH for _ in range(4): # run instructions for char in instructions: if char == "G": self.move(position, direction) else: direction = self.change_direction(direction, char) # check if back to start if position[0] == 0 and position[1] == 0: return True return False def move(self, position, direction): if direction == Direction.NORTH: position[1] = position[1]+1 elif direction == Direction.SOUTH: position[1] = position[1]-1 elif direction == Direction.EAST: position[0] = position[0]+1 elif direction == Direction.WEST: position[0] = position[0]-1 def change_direction(self, direction, change): if change == "L": if direction == Direction.NORTH: return Direction.WEST elif direction == Direction.SOUTH: return Direction.EAST elif direction == Direction.EAST: return Direction.NORTH elif direction == Direction.WEST: return Direction.SOUTH if change == "R": if direction == Direction.NORTH: return Direction.EAST elif direction == Direction.SOUTH: return Direction.WEST elif direction == Direction.EAST: return Direction.SOUTH elif direction == Direction.WEST: return Direction.NORTH """ --------------------------------------------- """ class Solution1: def isRobotBounded(self, instructions: str): position = [0, 0] direction = Direction.NORTH for char in instructions: if char == "G": self.move(position, direction) else: direction = self.change_direction(direction, char) # check if back to start if position[0] == 0 and position[1] == 0: return True # check if changed direction return direction != Direction.NORTH def move(self, position, direction): if direction == Direction.NORTH: position[1] = position[1]+1 elif direction == Direction.SOUTH: position[1] = position[1]-1 elif direction == Direction.EAST: position[0] = position[0]+1 elif direction == Direction.WEST: position[0] = position[0]-1 def change_direction(self, direction, change): if change == "L": if direction == Direction.NORTH: return Direction.WEST elif direction == Direction.SOUTH: return Direction.EAST elif direction == Direction.EAST: return Direction.NORTH elif direction == Direction.WEST: return Direction.SOUTH if change == "R": if direction == Direction.NORTH: return Direction.EAST elif direction == Direction.SOUTH: return Direction.WEST elif direction == Direction.EAST: return Direction.SOUTH elif direction == Direction.WEST: return Direction.NORTH """ --------------------------------------------- """ # same as above but using math tricks class Solution2: def isRobotBounded(self, instructions: str): direction = (0, 1) start = [0, 0] for x in instructions: if x == 'G': start[0] += direction[0] start[1] += direction[1] elif x == 'L': direction = (-direction[1], direction[0]) elif x == 'R': direction = (direction[1], -direction[0]) # check if back to start or if changed direction return start == [0, 0] or direction != (0, 1) -
https://leetcode.com/problems/integer-to-english-words/

Screen Recording 2021-10-15 at 21.00.14.mov
""" This problem is about the decomposition of the problem -- how do you break it down. Not about efficiency. max => 2,147,483,647 ("Two Billion - One Hundred Forty Seven Million - Four Hundred Eighty Three Thousand - Six Hundred Forty Seven") the `len_three` function and how it's used is what you should understand """ class Solution: def len_one(self, num): store = {1: 'One', 2: 'Two', 3: 'Three', 4: 'Four', 5: 'Five', 6: 'Six', 7: 'Seven', 8: 'Eight', 9: 'Nine'} return store[num] def len_two(self, num): tens_less_20 = {10: 'Ten', 11: 'Eleven', 12: 'Twelve', 13: 'Thirteen', 14: 'Fourteen', 15: 'Fifteen', 16: 'Sixteen', 17: 'Seventeen', 18: 'Eighteen', 19: 'Nineteen'} tens_greater_20 = {2: 'Twenty', 3: 'Thirty', 4: 'Forty', 5: 'Fifty', 6: 'Sixty', 7: 'Seventy', 8: 'Eighty', 9: 'Ninety'} if num < 10: return self.len_one(num) elif num < 20: return tens_less_20[num] # tens > 20 elif num >= 20: tens = num // 10 ones = num % 10 if ones: return tens_greater_20[tens] + ' ' + self.len_one(ones) else: return tens_greater_20[tens] return '' def len_three(self, num): hundred = num // 100 rest = num % 100 if hundred and rest: return self.len_one(hundred) + ' Hundred ' + self.len_two(rest) elif hundred and not rest: return self.len_one(hundred) + ' Hundred' elif not hundred and rest: return self.len_two(rest) return '' # not needed def numberToWords(self, num): # special case if not num: return 'Zero' billion = num // 1000000000 million = (num - billion * 1000000000) // 1000000 thousand = (num - billion * 1000000000 - million * 1000000) // 1000 rest = num - billion * 1000000000 - million * 1000000 - thousand * 1000 result = '' if billion: result = self.len_three(billion) + ' Billion' if million: result += ' ' if result else '' result += self.len_three(million) + ' Million' if thousand: result += ' ' if result else '' result += self.len_three(thousand) + ' Thousand' if rest: result += ' ' if result else '' result += self.len_three(rest) return result -
Add Binary
Screen Recording 2021-10-15 at 21.29.59.mov
""" Add Binary Given two binary strings a and b, return their sum as a binary string. Example 1: Input: a = "11", b = "1" Output: "100" Example 2: Input: a = "1010", b = "1011" Output: "10101" https://leetcode.com/problems/add-binary """ class Solution: def addBinary(self, a: str, b: str): n = max(len(a), len(b)) res = [0]*(n+1) one_idx = len(a)-1 two_idx = len(b)-1 for idx in reversed(range(n+1)): carry = res[idx] one = 0 two = 0 if one_idx >= 0: one = int(a[one_idx]) one_idx -= 1 if two_idx >= 0: two = int(b[two_idx]) two_idx -= 1 addition = one + two + carry res[idx] = addition % 2 # save result # save carry if addition // 2: # prevent saving carry in idx 0 res[idx-1] = addition // 2 # remove preceeding zeros start_idx = 0 while res[start_idx] == 0 and start_idx < len(res)-1: start_idx += 1 res = res[start_idx:] return "".join([str(item) for item in res]) -
https://leetcode.com/problems/evaluate-division/
Find the original version of this page (with additional content) on Notion here.
Created: December 13, 2021 16:05:48