K-Way Merge
Introduction
This pattern helps us solve problems that involve a list of sorted arrays.
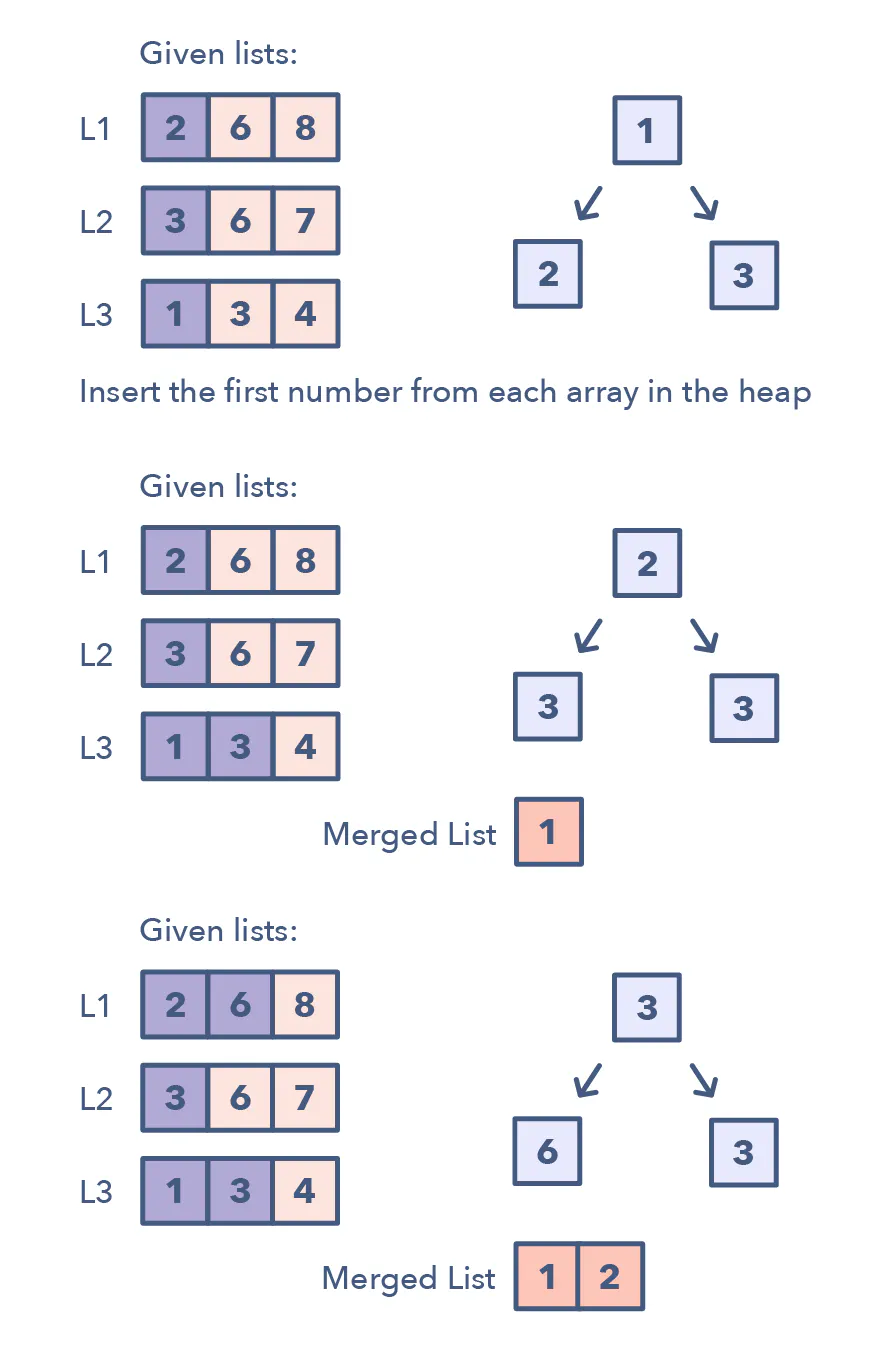
Whenever we are given ‘K’ sorted arrays, we can use a Heap to efficiently perform a sorted traversal of all the elements of all arrays. We can push the smallest (first) element of each sorted array in a Min Heap to get the overall minimum. While inserting elements to the Min Heap we keep track of which array the element came from. We can, then, remove the top element from the heap to get the smallest element and push the next element from the same array, to which this smallest element belonged, to the heap. We can repeat this process to make a sorted traversal of all elements.
When to use
Whenever you’re given ‘K’ sorted arrays, you can use a Heap to efficiently perform a sorted traversal of all the elements of all arrays. You can push the smallest element of each array in a Min Heap to get the overall minimum. After getting the overall minimum, push the next element from the same array to the heap. Then, repeat this process to make a sorted traversal of all elements.
Merge K Sorted Lists
Problem
"""
Merge K Sorted Lists:
You are given an array of k linked-lists lists, each linked-list is sorted in ascending order.
Merge all the linked-lists into one sorted linked-list and return it.
Example 1:
Input: lists = [[1,4,5],[1,3,4],[2,6]]
Output: [1,1,2,3,4,4,5,6]
Explanation: The linked-lists are:
[
1->4->5,
1->3->4,
2->6
]
merging them into one sorted list:
1->1->2->3->4->4->5->6
Example 2:
Input: lists = []
Output: []
Example 3:
Input: lists = [[]]
Output: []
Example 4:
Input: L1=[2, 6, 8], L2=[3, 6, 7], L3=[1, 3, 4]
Output: [1, 2, 3, 3, 4, 6, 6, 7, 8]
Example 5:
Input: L1=[5, 8, 9], L2=[1, 7]
Output: [1, 5, 7, 8, 9]
https://leetcode.com/problems/merge-k-sorted-lists/
https://www.educative.io/courses/grokking-the-coding-interview/Y5n0n3vAgYK
"""
Solution
from typing import List
import heapq
"""
Solution:
[[1,4,5],[1,3,4],[2,6]]
Output: [1,1,2,3,4,4,5,6]
# Non-optimal Solution:
using pointers ->
Time complexity : O(kN) where k is the number of linked lists.
Almost every selection of node in final linked costs O(k) time. There are N nodes in the final linked list.
There are NN nodes in the final linked list.
- for each list, create a pointer to the head of the list
- compare the values of the pointers, and add the smaller value to the result list
# Optimal Solution:
using heap ->
Time complexity : O(klogk) where k is the number of linked lists.
- add the first element of each list to a heap (keep track of the list((index or node) and the value))
- while the heap is not empty:
- pop the smallest element from the heap and add it to the result list
- add the next element of the list to the heap
- return the result list
"""
# Definition for singly-linked list.
class ListNode:
def __init__(self, val=0, next=None):
self.val = val
self.next = next
# --------
class Solution0:
def mergeKLists(self, lists: List[ListNode]):
heap = [] # added in the form [val, random_unique_key, node]
for i in range(len(lists)):
if lists[i] is not None:
heap.append([lists[i].val, i, lists[i]])
heapq.heapify(heap)
res = ListNode()
curr = res
while len(heap) > 0:
# remove the smallest element
smallest_arr = heapq.heappop(heap)
curr.next = ListNode(smallest_arr[0])
curr = curr.next
# add the next node in the list that contains the smallest_arr[2] element
nxt = smallest_arr[2].next
if nxt is not None:
heapq.heappush(heap, [nxt.val, smallest_arr[1], nxt])
return res.next
# --------
class HeapElement:
def __init__(self, val, node):
self.val = val
self.node = node
def __gt__(self, other): # (greater than) will be used in comparisons by the heap
return self.val > other.val
class Solution:
def mergeKLists(self, lists: List[ListNode]):
# add the first element of each list to a heap
heap = []
for i in range(len(lists)):
if lists[i] is not None:
heap.append(HeapElement(lists[i].val, lists[i]))
heapq.heapify(heap)
res = ListNode()
curr = res
while len(heap) > 0:
# remove the smallest element
smallest = heapq.heappop(heap)
# add to res
curr.next = ListNode(smallest.val)
curr = curr.next
# add the next node in the list that contains the smallest[2] element
if smallest.node.next is not None:
heapq.heappush(heap, HeapElement(smallest.node.next.val,
smallest.node.next)
)
return res.next # skip the one used initialise res
Non-optimal Solution
Kth Smallest Number in M Sorted Lists
"""
Kth Smallest Number in M Sorted Lists:
Given ‘M’ sorted arrays, find the K’th smallest number among all the arrays.
Example 1:
Input: L1=[2, 6, 8], L2=[3, 6, 7], L3=[1, 3, 4], K=5
Output: 4
Explanation: The 5th smallest number among all the arrays is 4, this can be verified from
the merged list of all the arrays: [1, 2, 3, 3, 4, 6, 6, 7, 8]
Example 2:
Input: L1=[5, 8, 9], L2=[1, 7], K=3
Output: 7
Explanation: The 3rd smallest number among all the arrays is 7.
"""
"""
L1=[2, 6, 8], L2=[3, 6, 7], L3=[1, 3, 4], K=5
- initialise heap with the first element of each list
- pop the smallest element from the heap and replace it with the next element from the list it came from
- repeat until the K'th time and return the number
"""
import heapq
class HeapElement:
def __init__(self, val, val_idx, list_idx):
self.val = val
self.val_idx = val_idx
self.list_idx = list_idx
def __gt__(self, other):
return self.val > other.val
def get_list(self, arr):
return arr[self.list_idx]
def find_Kth_smallest(lists, k):
heap = []
for i in range(len(lists)):
if len(lists[i]) > 0:
heapq.heappush(heap, HeapElement(lists[i][0], 0, i))
number = -1
for _ in range(k):
if len(heap) == 0:
return -1
smallest = heapq.heappop(heap)
# record number
number = smallest.val
# replace with next element from the list
if smallest.val_idx + 1 < len(smallest.get_list(lists)):
element = HeapElement(
smallest.get_list(lists)[smallest.val_idx + 1],
smallest.val_idx + 1,
smallest.list_idx
)
heapq.heappush(heap, element)
return number
print("Kth smallest number is: " +
str(find_Kth_smallest([[2, 6, 8], [3, 6, 7], [1, 3, 4]], 5)))
print("Kth smallest number is: " +
str(find_Kth_smallest([[2, 6, 8], [3, 6, 7], [1, 3, 4]], 2)))
print("Kth smallest number is: " +
str(find_Kth_smallest([[2, 6, 8], [3, 6, 7], [1, 3, 4]], 1)))
print("Kth smallest number is: " +
str(find_Kth_smallest([[2, 6, 8], [3, 6, 7], [1, 3, 4]], 200)))
Find the original version of this page (with additional content) on Notion here.
Created: December 13, 2021 16:05:48