Subsets, Permutations & Combinations *
Introduction

Subsets
A huge number of coding interview problems involve dealing with Permutations and Combinations of a given set of elements. This pattern describes an efficient Breadth-First Search (BFS) approach to handle all these problems.
Simple problems
Subsets
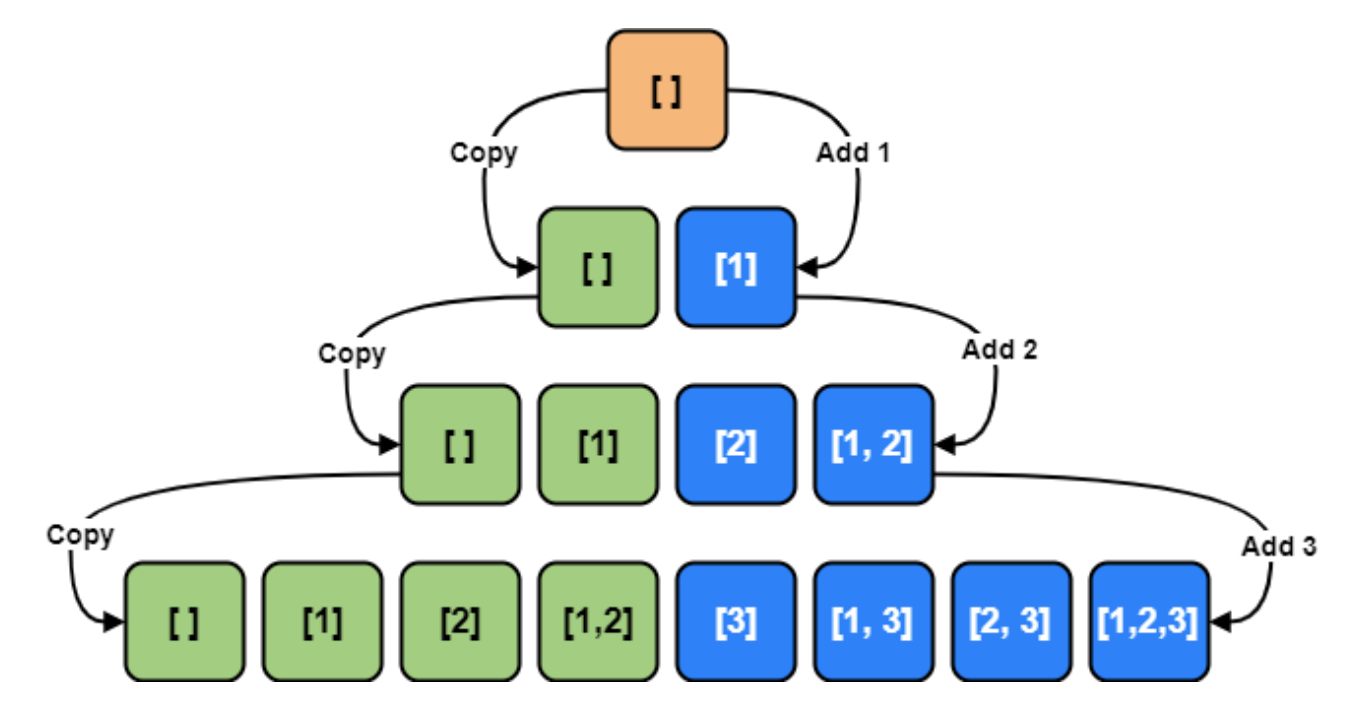
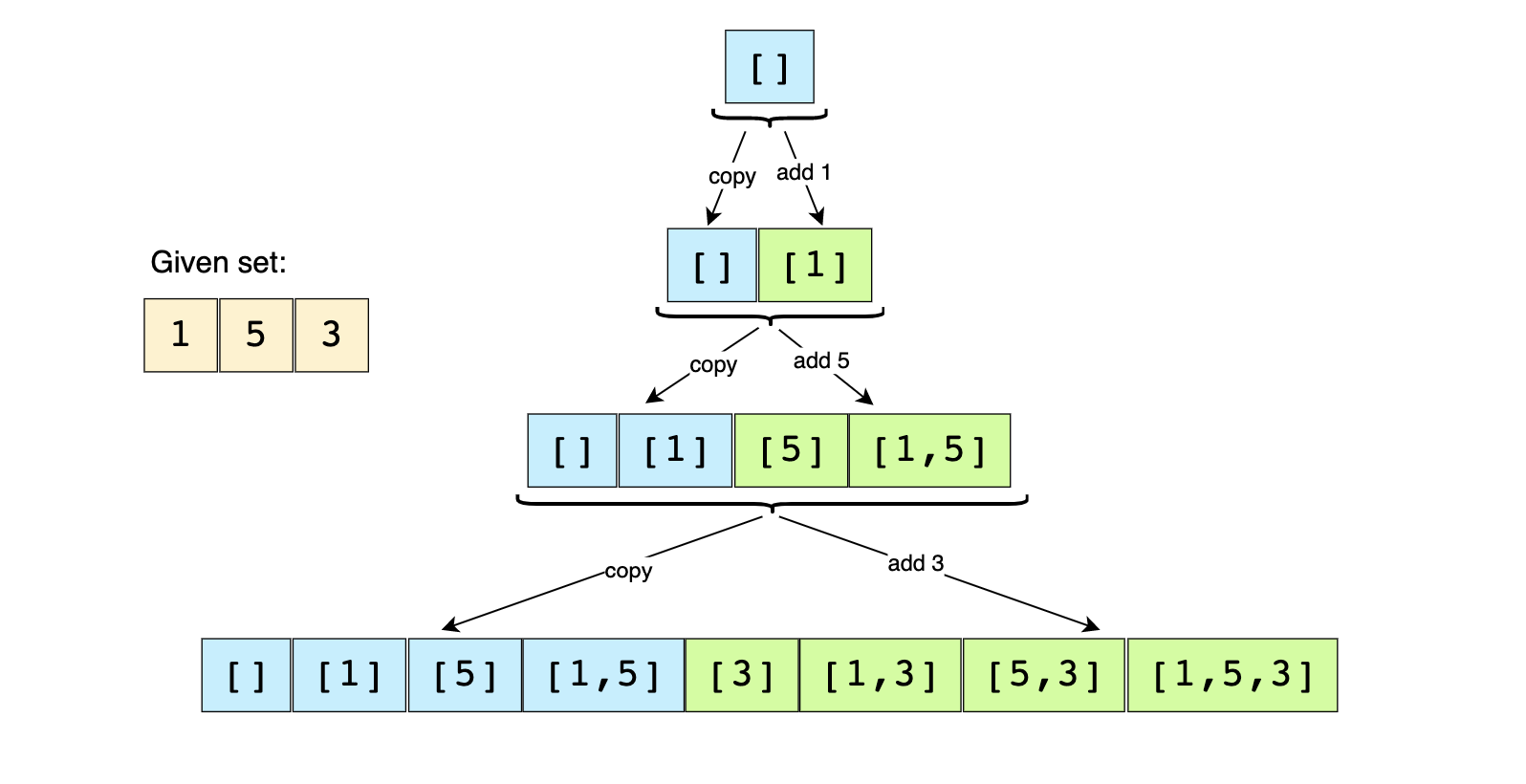
To generate all possible subsets, we can use the Breadth First Search (BFS) approach. Starting with an empty set, we will iterate through all numbers one-by-one, and add them to existing sets to create subsets.
- Start with an empty set: [[ ]]
- Add
num(1) to existing sets: [[ ], [1]] - Add
num(2) to existing sets: [[ ], [1], [2], [1, 2]] - Add
num(3) to existing sets: [[ ], [1], [2], [1, 2], [3], [1, 3], [2, 3], [1, 2, 3]]
"""
Subsets/Powerset:
Write a function that takes in an array of unique integers and returns its powerset.
The powerset P(X) of a set X is the set of all subsets of X.
For example, the powerset of [1,2] is [[], [1], [2], [1,2]].
Note that the sets in the powerset do not need to be in any particular order.
https://www.algoexpert.io/questions/Powerset
# https://leetcode.com/problems/subsets/
"""
"""
To generate all subsets of the given set, we can use the Breadth First Search (BFS) approach.
We can start with an empty set, iterate through all numbers one-by-one, and add them to existing sets to create new subsets.
"""
class Solution:
def subsets(self, nums: List[int]) -> List[List[int]]:
powerset = [[]]
for num in nums:
# take all existing subsets and add num to them
for i in range(len(powerset)):
powerset.append(powerset[i] + [num])
return powerset
Time Complexity: O(2^N) since, in each step, number of subsets doubles.
Each number can eitther be in a previous subsets or not. If we had an array of len 10, the number of subtrees at each level of the recursive tree will be: \(1 * 2 * 2 * 2 * 2 * 2 * 2 * 2 * 2 * 2 == 2 pow 10\)
Space Complexity: O(2^N)
Since, in each step, the number of subsets doubles as we add each element to all the existing subsets, therefore, we will have a total of **O(2^N)** subsets, where ‘N’ is the total number of elements in the input set. And since we construct a new subset from an existing set, therefore, the time complexity of the above algorithm will be O(N*2^N)
All the additional space used by our algorithm is for the output list. Since we will have a total of O(2^N) subsets, and each subset can take up to O(N) space, therefore, the space complexity of our algorithm will be O(N*2^N)
Subsets With Duplicates/Subsets II
"""
Subsets II
Given a collection of integers that might contain duplicates, nums, return all possible subsets (the power set).
Note: The solution set must not contain duplicate subsets.
Example:
Input: [1,2,2]
Output:
[
[2],
[1],
[1,2,2],
[2,2],
[1,2],
[]
]
https://leetcode.com/problems/subsets-ii/
"""
"""
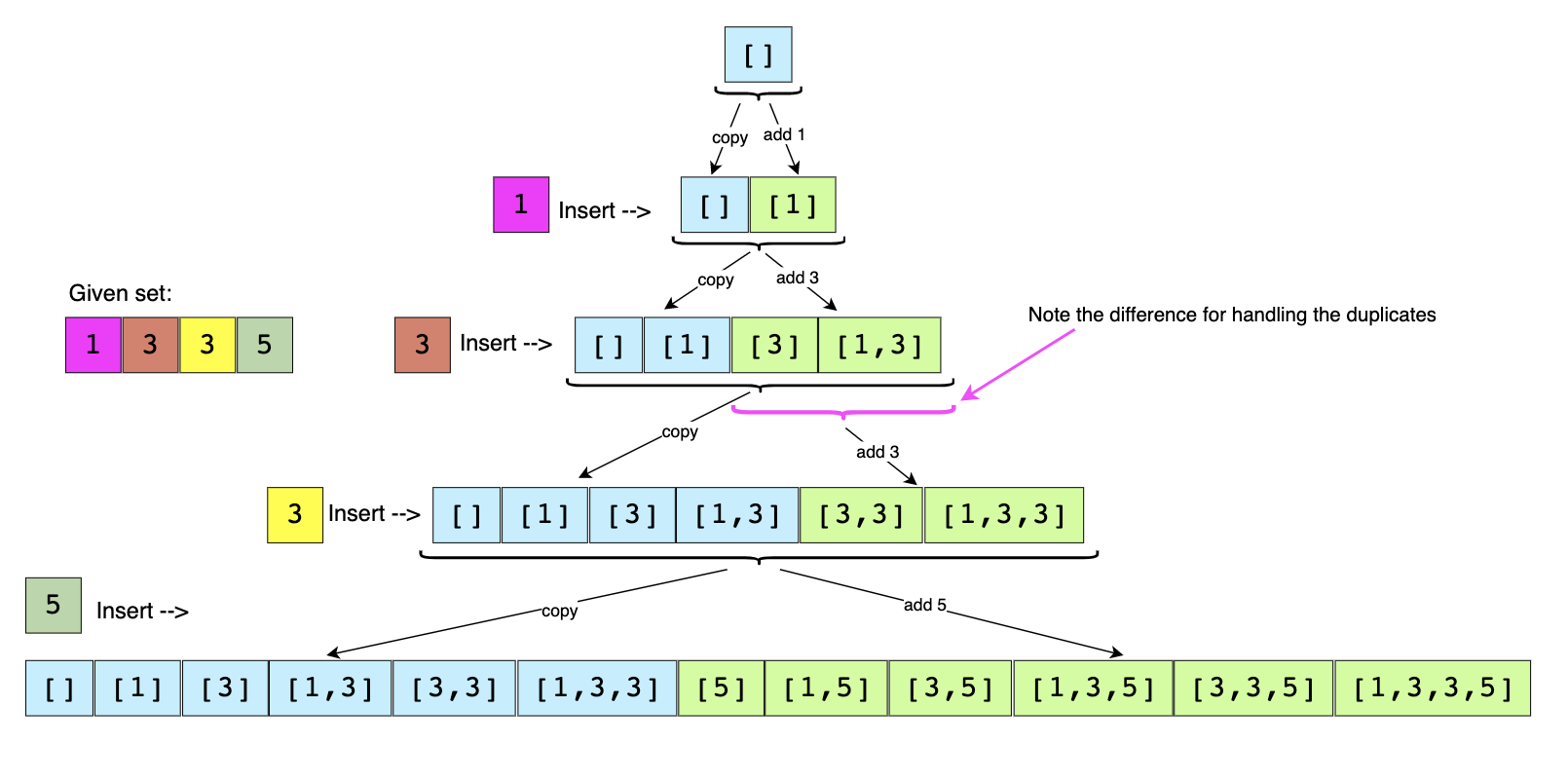
- Sort all numbers of the given set. This will ensure that all duplicate numbers are next to each other.
- When we process a duplicate ( instead of adding the current number (which is a duplicate) to all the existing subsets,
only add it to the subsets which were created in the previous step.
"""
class Solution:
def subsetsWithDup(self, nums: List[int]):
subsets = [[]]
nums.sort()
last_added = 0
for idx, num in enumerate(nums):
# handle duplicates
if idx > 0 and num == nums[idx-1]:
added = 0
for i in range(len(subsets)-last_added, len(subsets)):
subsets.append(subsets[i] + [num])
added += 1
last_added = added
# handle non-duplicates
else:
last_added = 0
for i in range(len(subsets)):
subsets.append(subsets[i] + [num])
last_added += 1
return subsets
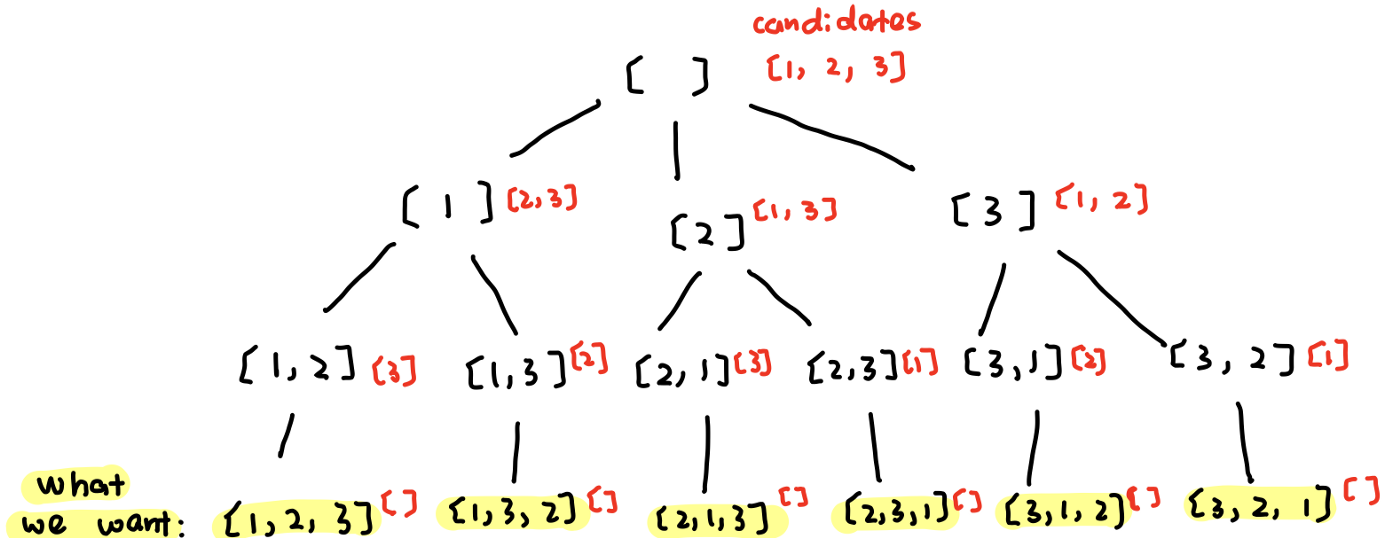
Permutations
Problem
"""
Permutations
Given an array nums of distinct integers, return all the possible permutations. You can return the answer in any order.
Example 1:
Input: nums = [1,2,3]
Output: [[1,2,3],[1,3,2],[2,1,3],[2,3,1],[3,1,2],[3,2,1]]
https://leetcode.com/problems/permutations/
https://www.algoexpert.io/questions/Permutations
"""
Solution
Screen Recording 2021-10-30 at 22.34.05.mov
Solution one
"""
[
[1,2,3],
[1,3,2],
[2,1,3],
[2,3,1],
[3,1,2],
[3,2,1]
]
[]
/ | \
[1] [2]
/ \ / \
[1,2] [1,3] [2,1] [2,3]
| | | |
[1,2,3] [1,3,2] [2,1,3] [2,3,1]
([], [], [1,2,3])
([], [1], [2,3]) ([], [2], [1,3]) ([], [3], [1,2])
([], [1, 2], [3]) ([], [1, 3], [3])
[[1,2,3,4],[1,2,4,3],[1,3,2,4],[1,3,4,2],[1,4,2,3],[1,4,3,2],[2,1,3,4],[2,1,4,3],[2,3,1,4],[2,3,4,1],[2,4,1,3],[2,4,3,1],[3,1,2,4],[3,1,4,2],[3,2,1,4],[3,2,4,1],[3,4,1,2],[3,4,2,1],[4,1,2,3],[4,1,3,2],[4,2,1,3],[4,2,3,1],[4,3,1,2],[4,3,2,1]]
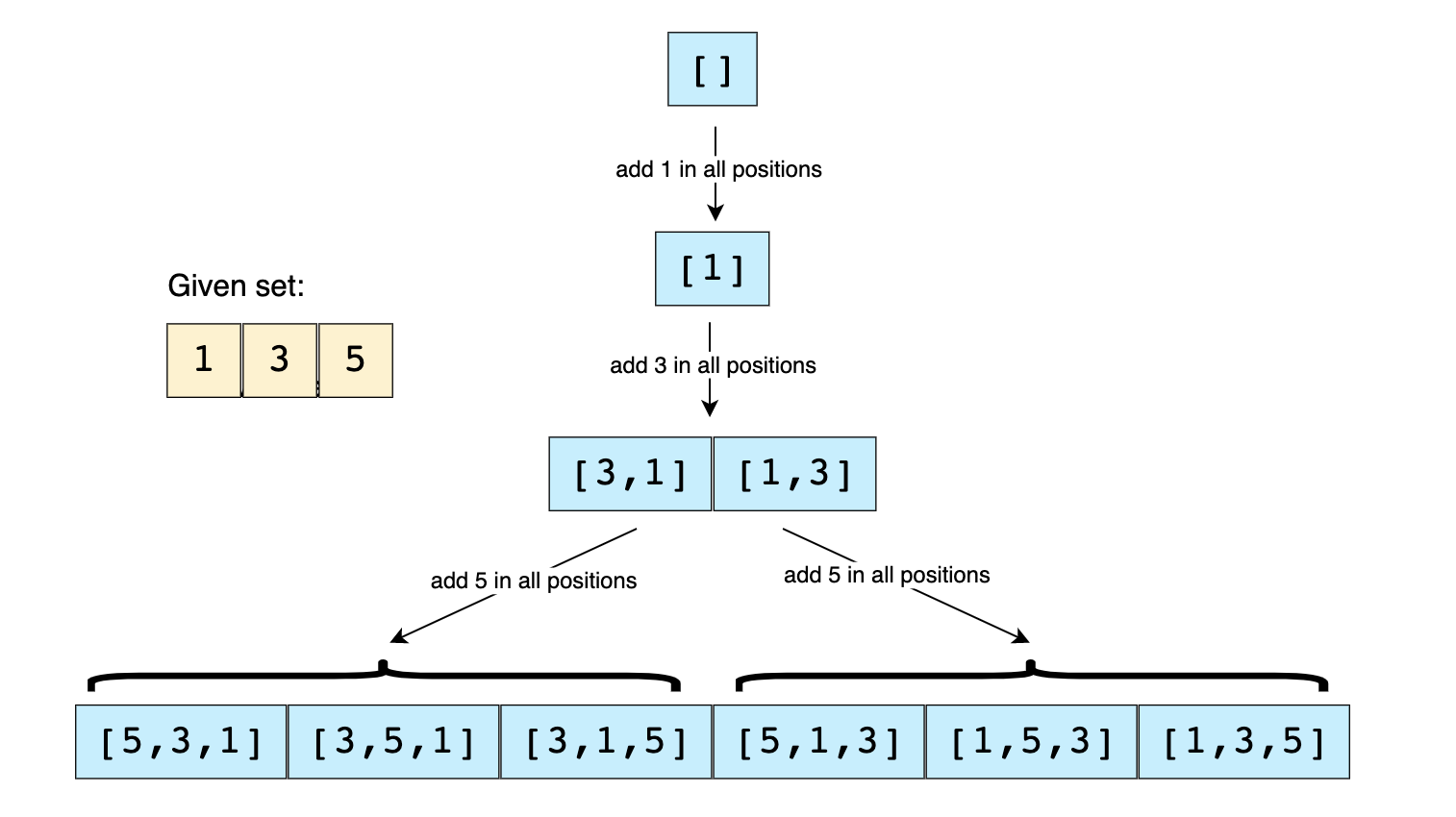
# try placing each number at the beginning if the list, then add all the others at all the possible positions
- have result = []
- have a function perm(arr, curr_subset, result)
- for each num in arr
- place num in a copy of curr_subset
- remove the num in a copy of arr
- pass both copies to perm()
- do the above step till arr is empty
- then add curr_subset to result
- return result
"""
def _getPermutationsHelper(array, result, curr):
if not array:
return result.append(curr)
for i in range(len(array)):
_getPermutationsHelper(array[:i]+array[i+1:], result, curr+[array[i]])
def _getPermutations(array):
result = []
if not array:
return result
_getPermutationsHelper(array, result, [])
return result
Solution two
"""
# remove all the elements from nums then insert them back in all positions possible
# place one each number at the beginning of a different list, then insert all the rest in different orders
- have a recursive function perm(nums_array)
- with base cases:
returns [[]] once nums_array is empty
- for each number in the list (iterate through the list)
- remove it from the list
- pass the rest of the numbers to the perm() recursive function
- add it to all the lists returned by perm()
"""
def getPermutations0(array):
if len(array) == 1:
return [array[:]]
result = []
for _ in range(len(array)):
# use the first index by default instead of keeping track of indices down the recursive tree
num = array.pop(0)
for arr in getPermutations(array):
arr.append(num)
result.append(arr)
array.append(num)
return result
# look below for an alternative
"""
Improvement of above
"""
def ___getPermutations(array):
if len(array) < 1:
return array
return ___getPermutationsHelper(array, 0)
def ___getPermutationsHelper(array, pos):
if pos == len(array)-1:
return [[array[pos]]]
result = []
for i in range(pos, len(array)):
# add the number(array[i]) to the permutation
# place the element of interest at the first position (pos)
# Example: for getPermutationsHelper([1,2,3,4], 0), while in this for loop
# when at value 1 (i=0), we want 1 to be at pos(0), so that we can iterate through [2,3,4] next without adding 1 again
# when at 2, we want 2 to be at pos(0), so that we can iterate through [1,3,4] next ([2,1,3,4])
# when at 3, we want it to be at pos(0), so that we can iterate through [2,1,4] next ([3,2,1,4])
# so we have to manually place it there (via swapping with the element at pos), then we return it just before the loop ends
# and move pos forward
# # num = array[i] (num of interest)
# place the num at pos because it will be ignored down the recursive tree
array[i], array[pos] = array[pos], array[i]
for subset in ___getPermutationsHelper(array, pos+1):
subset.append(array[pos])
result.append(subset)
# return num to its original position
array[i], array[pos] = array[pos], array[i]
return result
Solution three (most optimal)
"""
perm(1,2,3)
[1,2,3]
/ | \
[1,2,3] [2,1,3] [3,2,1]
/ \ / \ / \
[1,2,3] [1,3,2] [2,1,3] [2,3,1] [3,2,1] [3,1,2]
Try to get all possible arrangements of nums
"""
def getPermutations(array):
if len(array) < 1:
return array
result = []
getPermutationsHelper(result, array, 0)
return result
def getPermutationsHelper(result, array, pos):
if pos == len(array):
result.append(array[:]) # found one arrangement
return
for i in range(pos, len(array)):
# # add the number(array[i]) to the permutation
# place the element of interest at the first position (pos)
# Example: for getPermutationsHelper([1,2,3,4], 0), while in this for loop
# when at value 1 (i=0), we want 1 to be at pos(0), so that we can iterate through [2,3,4] next without adding 1 again
# when at 2, we want 2 to be at pos(0), so that we can iterate through [1,3,4] next ([2,1,3,4])
# when at 3, we want it to be at pos(0), so that we can iterate through [2,1,4] next ([3,2,1,4])
# so we have to manually place it there (via swapping with the element at pos), then we return it just before the loop ends
# and move pos forward
# # num = array[i] (num of interest) -> it is array[i]'s turn to be at pos
# place the num at pos because it will be ignored down the recursive tree
array[i], array[pos] = array[pos], array[i]
getPermutationsHelper(result, array, pos+1)
# return num to its original position
array[i], array[pos] = array[pos], array[i]
Time & Space complexity

-
Time complexity: O(n x n!) as there are n! permutations and n for the cost of list slicing.
N * (N-1) * ... * ! == 3 * 2 * 1 == N!
We know that there are a total of
N!permutations of a set with ‘N’ numbers. In the algorithm above, we are iterating through all of these permutations with the help of the two ‘for’ loops. In each iteration, we go through all the current permutations to insert a new number in them on line 17 (line 23 for C++ solution). To insert a number into a permutation of size ‘N’ will take O(N), which makes the overall time complexity of our algorithmO(N*N!).If we had an array of len 10, the number of subtrees at each level of the recursive tree will be: \(10 * 9 * 8 * 7 * 6 * 5 * 4 * 3 * 2 * 1 == 10!\)
- Space complexity:
O(N*N!)as we have to store all n! permutations and for each permutation, we store a slice of the input.
- Space complexity:
Permutations with duplicates
Letter Case Permutations/String Permutations by changing case
"""
Letter Case Permutation/String Permutations by changing case:
Given a string s, we can transform every letter individually to be lowercase or uppercase to create another string.
Return a list of all possible strings we could create. You can return the output in any order.
Example 1:
Input: s = "a1b2"
Output: ["a1b2","a1B2","A1b2","A1B2"]
Example 2:
Input: s = "3z4"
Output: ["3z4","3Z4"]
Example 3:
Input: s = "12345"
Output: ["12345"]
Example 4:
Input: s = "0"
Output: ["0"]
https://leetcode.com/problems/letter-case-permutation/
"""
"""
Brute force:
- result = []
- have a perm(s,idx,curr_perm) helper function
- for the character at idx:
perm(s, idx+1, curr_perm+[character])
- if is not a number:
perm(s, idx+1, curr_perm+[character.swapcase()])
- once we reach idx == len(s):
- result.append(curr_perm)
---
Optimal:
- result = []
- arr = list(s)
- have a perm(arr,idx) helper function
- for the character at idx:
perm(arr,idx+1)
- if is not a number:
arr[idx] = arr[idx].swapcase()
perm(arr,idx+1)
arr[idx] = arr[idx].swapcase()
- once we reach idx == len(s):
- result.append(arr[:])
https://leetcode.com/problems/letter-case-permutation/discuss/379928/Python-clear-solution
"""
class Solution:
def letterCasePermutationHelper(self, result, arr, idx):
if idx == len(arr):
result.append("".join(arr))
return
# case 1: do nothing
self.letterCasePermutationHelper(result, arr, idx+1)
# case 2: change case
if arr[idx].isalpha():
arr[idx] = arr[idx].swapcase()
self.letterCasePermutationHelper(result, arr, idx+1)
arr[idx] = arr[idx].swapcase()
def letterCasePermutation(self, s):
result = []
if len(s) < 1:
return result
self.letterCasePermutationHelper(result, list(s), 0)
return result
More examples
Combinations
Combination Sum
Find the original version of this page (with additional content) on Notion here.
Created: December 13, 2021 16:05:48