Divide and Conquer
Introduction to Divide and Conquer With Binary Search - Algorithms for Coding Interviews in Python
DAA Divide and Conquer Introduction - javatpoint
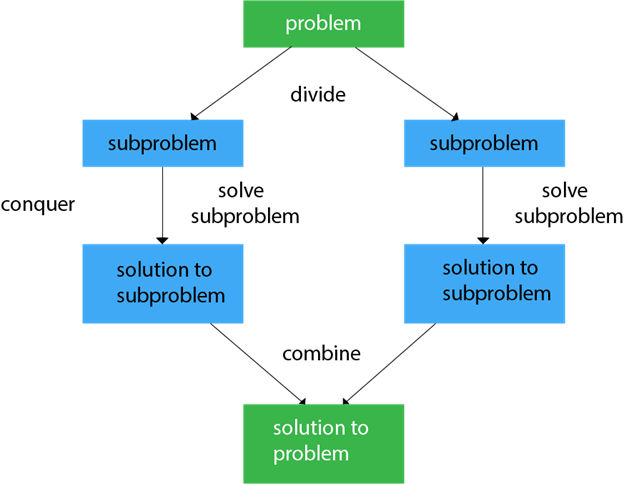
In divide and conquer approach, a problem is divided into smaller problems, then the smaller problems are solved independently, and finally the solutions of smaller problems are combined into a solution for the large problem.
Divide and conquer is an algorithmic paradigm in which the problem is repeatedly divided into subproblems until we reach a point where each problem is similar and atomic, i.e., can’t be further divided. At this point, we start solving these atomic problems and combining (merging) the solutions.
Generally, divide-and-conquer algorithms have three parts:
- Divide the problem into a number of sub-problems that are smaller instances of the same problem.
- Conquer the sub-problems by solving them recursively. If they are small enough, solve the sub-problems as base cases.
- Combine the solutions to the sub-problems into the solution for the original problem.
Examples
- Binary Search
- Quicksort: It is the most efficient sorting algorithm, which is also known as partition-exchange sort. It starts by selecting a pivot value from an array followed by dividing the rest of the array elements into two sub-arrays. The partition is made by comparing each of the elements with the pivot value. It compares whether the element holds a greater value or lesser value than the pivot and then sort the arrays recursively.
- Merge Sort: It is a sorting algorithm that sorts an array by making comparisons. It starts by dividing an array into sub-array and then recursively sorts each of them. After the sorting is done, it merges them back.
- Tower of Hanoi problem
Find the original version of this page (with additional content) on Notion here.
Created: December 13, 2021 16:05:48