Two Pointers
Introduction
Introduction - Grokking the Coding Interview: Patterns for Coding Questions
Sum MegaPost - Python3 Solution with a detailed explanation - LeetCode Discuss
In problems where we deal with sorted arrays (or LinkedLists) and need to find a set of elements that fulfill certain constraints, the Two Pointers approach becomes quite useful. The set of elements could be a pair, a triplet or even a subarray. For example, take a look at the following problem:
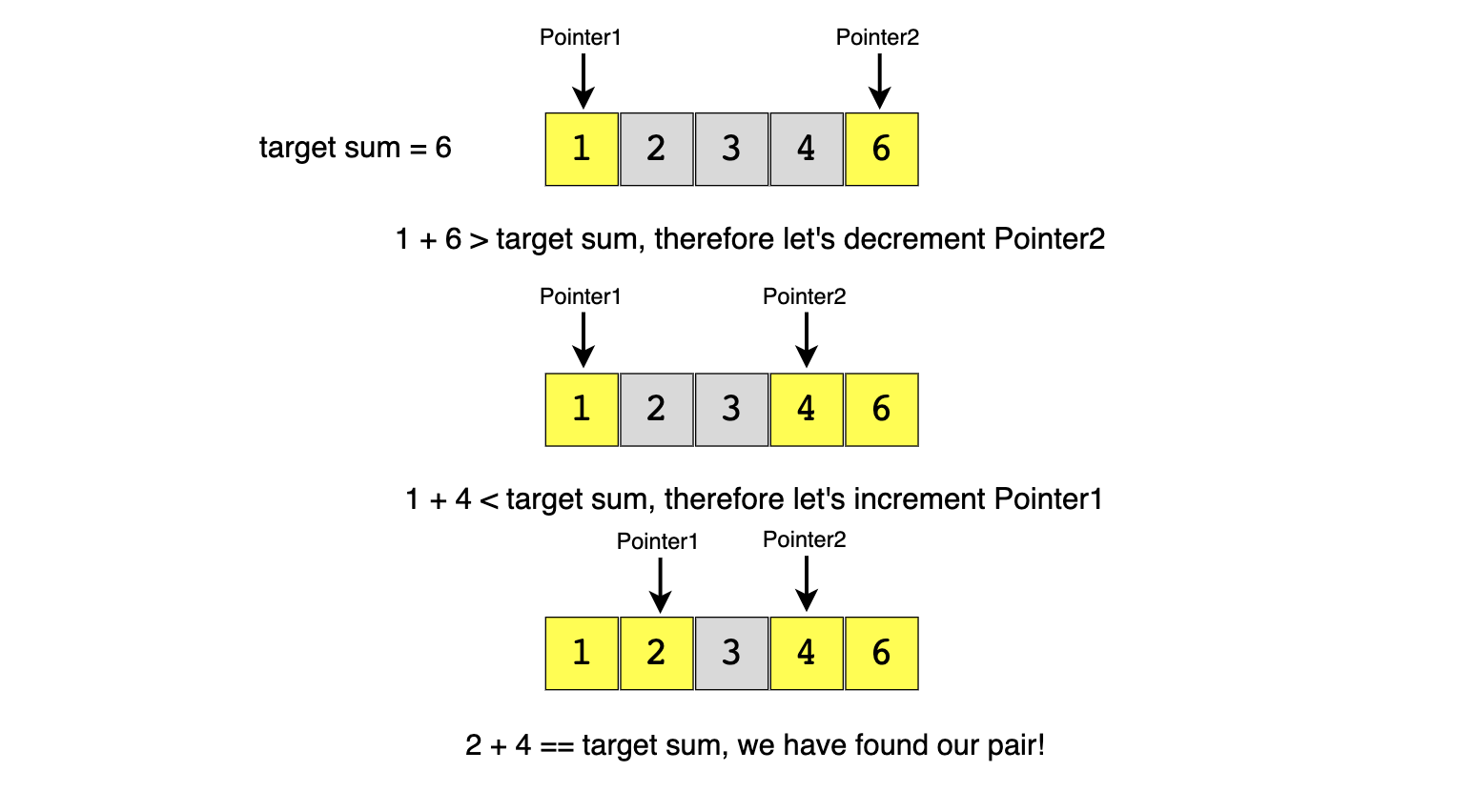
Given an array of sorted numbers and a target sum, find a pair in the array whose sum is equal to the given target.
To solve this problem, we can consider each element one by one (pointed out by the first pointer) and iterate through the remaining elements (pointed out by the second pointer) to find a pair with the given sum. The time complexity of this algorithm will be O(N^2) where ‘N’ is the number of elements in the input array.
Given that the input array is sorted, an efficient way would be to start with one pointer in the beginning and another pointer at the end. At every step, we will see if the numbers pointed by the two pointers add up to the target sum. If they do not, we will do one of two things:
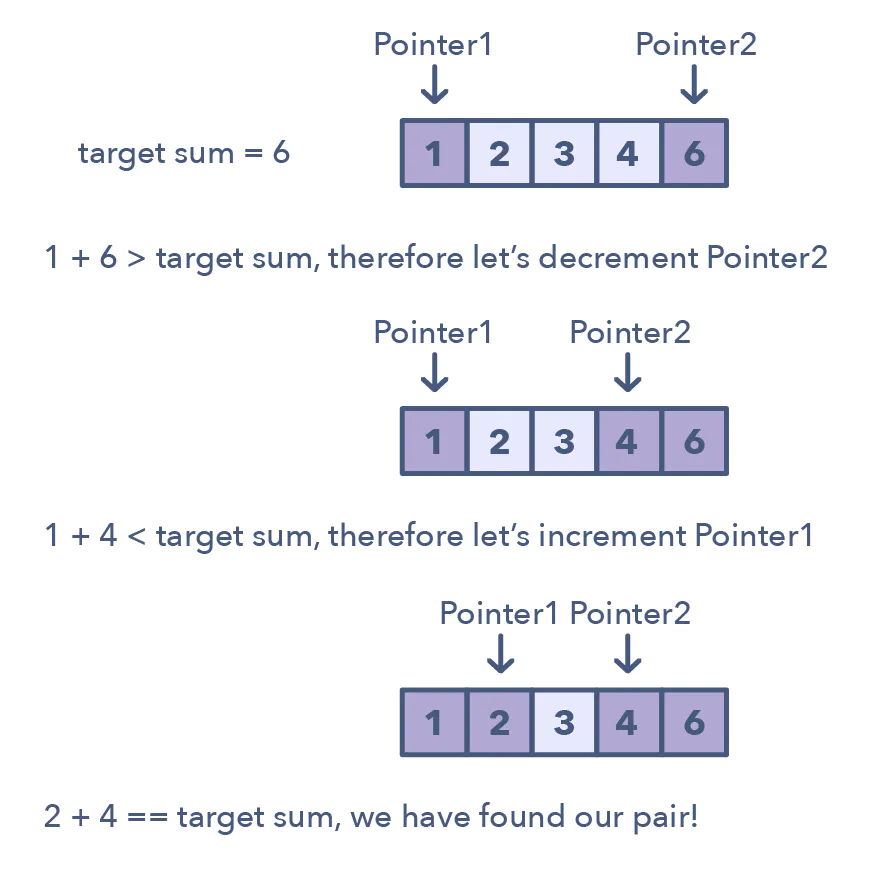
- If the sum of the two numbers pointed by the two pointers is smaller than the target sum, this means that we need a pair with a larger sum. So, to try more pairs, we can increment the start-pointer.
- If the sum of the two numbers pointed by the two pointers is greater than the target sum, this means that we need a pair with a smaller sum. So, to try more pairs, we can decrement the end-pointer.
The time complexity of the above algorithm will be O(N).
Two pointers are needed because with just pointer, you would have to continually loop back through the array to find the answer. This back and forth with a single iterator is inefficient for time and space complexity. While the brute force or naive solution with 1 pointer would work, it will produce something along the lines of O(n²). In many cases, two pointers can help you find a solution with better space or runtime complexity.
Simple problems
Two sum
For differences:
"""
Pair with Target Sum;
Given an array of sorted numbers and a target sum, find a pair in the array whose sum is equal to the given target.
https://www.educative.io/courses/grokking-the-coding-interview/xog6q15W9GP
"""
"""
- we need to search for two numbers
- we can have two pointers, one at the beginning and one at the end then check how their sum compares to the target
- if equal, return them
- if less than, increase the total sum by moving the left pointer forward
- if greater than, decrease the total sum by moving the right pointer backward
[1, 2, 3, 4, 6], target=6
l=1,r=6
l=1,r=4
l=2,r=4
"""
# O(1) space | O(n) time
def pair_with_targetsum(arr, target_sum):
left = 0
right = len(arr)-1
while left < right:
total = arr[left]+arr[right]
if total < target_sum:
left += 1
elif total > target_sum:
right -= 1
else:
return [arr[left], arr[right]]
return [-1, -1]

Check if number the current in the past using complements
Remove Duplicates
"""
Remove Duplicates;
Given an array of sorted numbers, remove all duplicates from it.
You should not use any extra space; after removing the duplicates in-place return the length of the subarray that has no duplicate in it.
"""
"""
Solution 1;
- have a res_length variable that will be initialised as 1
- have two pointers both at the start of the array: left & right
- move the right pointer one step forward:
- if its value is not equal to left's value, increment the value of res_length & move the left pointer to right's position
- if equal, repeat this step (move the right pointer one step forward)
[2, 3, 3, 3, 6, 9, 9]
l=2,r=2,res=1
l=3,r=3,res=2
l=3,r=3,res=2
l=3,r=3,res=2
l=6,r=6,res=3
l=9,r=9,res=4
l=9,r=9,res=4
"""
def remove_duplicates(arr):
res_length = 1
last_non_dup = 0
for idx in range(1, len(arr)):
if arr[last_non_dup] != arr[idx]:
res_length += 1
last_non_dup = idx
return res_length
"""
Solution 2:
In this problem, we need to remove the duplicates in-place such that the resultant length of the array remains sorted.
As the input array is sorted, therefore, one way to do this is to shift the elements left whenever we encounter duplicates.
In other words, we will keep one pointer for iterating the array and one pointer for placing the next non-duplicate number.
So our algorithm will be to iterate the array and whenever we see a non-duplicate number we move it next to the last non-duplicate number we’ve seen.
"""
def remove_duplicates2(arr):
next_non_duplicate = 1
for i in range(1, len(arr)):
if arr[next_non_duplicate - 1] != arr[i]:
arr[next_non_duplicate] = arr[i]
next_non_duplicate += 1
i += 1
return next_non_duplicate
Squaring a Sorted Array *
"""
Squaring a Sorted Array:
Given a sorted array, create a new array containing squares of all the numbers of the input array in the sorted order.
"""
"""
(arrange from largest to smallest then reverse)
- beacause our input array contains negative numbers,
the largest square can be either on the far right or far left
- so we need to iterate inwards (from outward):
- have a left & right pointer at both ends of the array and consider the largest square
Use two pointers starting at both ends of the input array.
At any step, whichever pointer gives us the bigger square,
we add it to the result array and move to the next/previous number according to the pointer.
"""
def make_squares(arr):
squares = []
left = 0
right = len(arr)-1
while left <= right:
left_s = arr[left] * arr[left]
right_s = arr[right] * arr[right]
if left_s > right_s:
squares.append(left_s)
left += 1
else:
squares.append(right_s)
right -= 1
squares.reverse()
return squares
Pairs with Specific Difference *
Three Sum
Problem
"""
Three Sum. (3Sum):
Triplet Sum to Zero:
Given an array nums of n integers, are there elements a, b, c in nums such that a + b + c = 0?
Find all unique triplets in the array which gives the sum of zero.
The solution set must not contain duplicate triplets.
Example 1:
Input: nums = [-1,0,1,2,-1,-4]
Output: [[-1,-1,2],[-1,0,1]]
Example 2:
Input: nums = []
Output: []
Example 3:
Input: nums = [0]
Output: []
https://www.educative.io/courses/grokking-the-coding-interview/gxk639mrr5r
"""
Solution
.
def search_triplets(nums):
nums.sort() # will make spotting of duplicates easy
triplets = []
length = len(nums)
for i in range(length-2): # ignore last two
# check if element is a duplicate. the first cannot be a duplicate
if i > 0 and nums[i] == nums[i-1]:
# skip handling an element if it's similar to the one before it
# because it is sorted, we effectively skip duplicates
continue
# TWO SUM for a sorted array
# 1. find elements that will add up to 0
# 2. check inner elements
left = i + 1
right = length - 1
while left < right:
total = nums[i] + nums[left] + nums[right]
if total < 0:
left += 1
elif total > 0:
right -= 1
# 1. add list of elements to triplets
# 2. move to inner elements
# 3. skip similar elements
else:
# add elements to triplets
triplets.append([nums[i], nums[left], nums[right]])
# skip:
# no need to continue with an element with the same value as l/r
# Skip all similar to the current left and right so that,
# when we are moving to the next element, we dont move to an element with the same value
while left < right and nums[left] == nums[left+1]:
left += 1
while left < right and nums[right] == nums[right-1]:
right -= 1
# move to inner elements
left += 1
right -= 1
return triplets
Time complexity
Sorting the array will take O(N log(N)). The searchPair/twoSum() function will take O(N).
As we are calling searchPair() for every number in the input array, this means that overall searchTriplets() will take O(N log(N) + N^2),which is asymptotically equivalent to O(N^2)
Four sum
Similar to three sum
"""
4Sum:
Given an array nums of n integers, return an array of all the unique quadruplets [nums[a], nums[b], nums[c], nums[d]] such that:
0 <= a, b, c, d < n
a, b, c, and d are distinct.
nums[a] + nums[b] + nums[c] + nums[d] == target
You may return the answer in any order.
Example 1:
Input: nums = [1,0,-1,0,-2,2], target = 0
Output: [[-2,-1,1,2],[-2,0,0,2],[-1,0,0,1]]
Example 2:
Input: nums = [2,2,2,2,2], target = 8
Output: [[2,2,2,2]]
"""
"""
[1,0,-1,0,-2,2]
[-2, -1, 0, 0, 1, 2]
- four sum is a combination of two two_sums
- sort the input array so that we can skip duplicates
- have two loops with to iterate through all the possible two number combinations:
- for the rest of the numbers: find a two sum that = target - (arr[idx_loop_one] + arr[idx_loop_two])
"""
class Solution:
def fourSum(self, nums, target):
res = []
nums.sort()
for one in range(len(nums)):
if one > 0 and nums[one] == nums[one-1]:
continue # skip duplicates
for two in range(one+1, len(nums)):
if two > one+1 and nums[two] == nums[two-1]:
continue # skip duplicates
# # two sum
needed = target - (nums[one] + nums[two])
left = two + 1
right = len(nums)-1
while left < right:
# skip duplicates
if left > two + 1 and nums[left] == nums[left-1]:
left += 1
continue
if right < len(nums)-1 and nums[right] == nums[right+1]:
right -= 1
continue
total = nums[left] + nums[right]
if total < needed:
left += 1
elif total > needed:
right -= 1
else:
res.append(
[nums[one], nums[two], nums[left], nums[right]])
left += 1
right -= 1
return res
Subarrays with Product Less than a Target *
Problem
"""
Subarrays with Product Less than a Target:
Given an array with positive numbers and a positive target number,
find all of its contiguous subarrays whose product is less than the target number.
Example 1:
Input: [2, 5, 3, 10], target=30
Output: [2], [5], [2, 5], [3], [5, 3], [10]
Explanation: There are six contiguous subarrays whose product is less than the target.
Example 2:
Input: [8, 2, 6, 5], target=50
Output: [8], [2], [8, 2], [6], [2, 6], [5], [6, 5]
Explanation: There are seven contiguous subarrays whose product is less than the target.
"""
Solution
"""
[2, 5, 2, 2, 3, 10], target=30
2=>2 [ [2],]
2,5=>10[[2], [2,5],[5]]
2,5,2=>20[[2],[2,5],[5], [2,5,2],[5,2],[2],]
# Add 2
2,5,2,2=>40
5,2,2=>20 -[[2],[2,5],[5],[2,5,2],[5,2],[2], [5,2,2],[2,2],[2],]
# Add 3
5,2,2,3=>60
2,2,3=>12 - [[2],[2,5],[5],[2,5,2],[5,2],[2], [5,2,2],[2,2],[2],]
# Add 10
2,2,3,10=>120
2,3,10=>60
3,10=>30 - [[2],[2,5],[5],[2,5,2],[5,2],[2],[5,2,2],[2,2],[2], [3,10], [10]]
#
"""
# O(n^3) time | O(n^3) space in the worst case
def find_subarrays(arr, target):
result = []
prod = 1
left = 0
for right in range(len(arr)):
# create window that has a prod < target
prod *= arr[right] # add right
while left <= right and prod >= target:
prod /= arr[left]
left += 1
# since the product of all numbers from left to right is less than the target therefore,
# all subarrays from left to right will have a product less than the target too;
# to avoid duplicates, we will start with a subarray containing only arr[right] and then extend it - done it the other way around here
# record result (all the subarrays of the current window ending with right)
# O(n^2) time | O(n^2) space in the worst case
for i in range(left, right+1):
result.append(arr[i:right+1])
return result
Time & Space complexity
Time
The main for-loop managing the sliding window takes O(N) but creating subarrays can take up to O(N^2) in the worst case. Therefore overall, our algorithm will take O(N^3)
Space
At most, we need space for O(n^2) output lists. At worst, each subarray can take O(n) space, so overall, our algorithm’s space complexity will be O(n^3)
Insert Intervals
"""
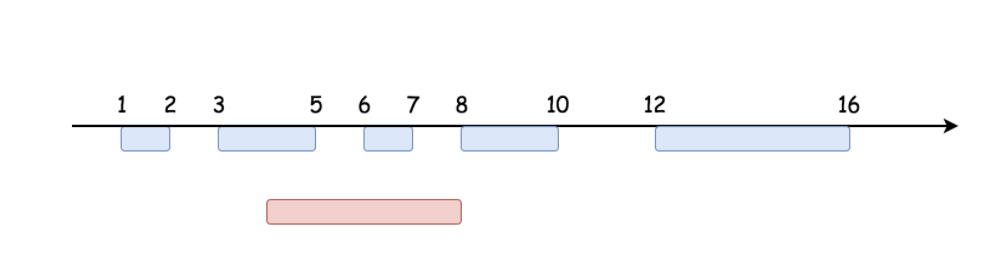
Insert Interval
You are given an array of non-overlapping intervals intervals where intervals[i] = [starti, endi] represent the start and the end of the ith interval
and intervals is sorted in ascending order by starti.
You are also given an interval newInterval = [start, end] that represents the start and end of another interval.
Insert newInterval into intervals such that intervals is still sorted in ascending order by starti and intervals still does not have any overlapping intervals (merge overlapping intervals if necessary).
Return intervals after the insertion.
Example 1:
Input: intervals = [[1,3],[6,9]], newInterval = [2,5]
Output: [[1,5],[6,9]]
Example 2:
Input: intervals = [[1,2],[3,5],[6,7],[8,10],[12,16]], newInterval = [4,8]
Output: [[1,2],[3,10],[12,16]]
Explanation: Because the new interval [4,8] overlaps with [3,5],[6,7],[8,10].
Example 3:
Input: intervals = [], newInterval = [5,7]
Output: [[5,7]]
Example 4:
Input: intervals = [[1,5]], newInterval = [2,3]
Output: [[1,5]]
Example 5:
Input: intervals = [[1,5]], newInterval = [2,7]
Output: [[1,7]]
https://leetcode.com/problems/insert-interval
"""
"""
intervals = [[1,2],[3,5],[6,7],[8,10],[12,16]], newInterval = [4,8]
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13
####
1-2 3---5 6-7 8---10 12----
4-------8
####
1---3 6-----9
4-------8
####
3---5 6-7 8---10
1-2
####
3---5 6-7 8---10
11-12
###
- res = []
- find the insert position (first interval with ending greater than newInterval's start)
- if None, add newInterval to the end
- else:
- add all before the start to res (Add to the output all the intervals starting before newInterval)
- add all overlaping intervals
while the current index's start < newInterval's end:
- update the newInterval's end to be the max of both ends
- skip it (interval at current index)(move index forward)
"""
from typing import List
class Solution__:
def insert(self, intervals: List[List[int]], newInterval: List[int]):
# - Find the insert position (first interval with ending greater than newInterval's start)
start_idx = -1
for idx, interval in enumerate(intervals):
if interval[1] >= newInterval[0]:
start_idx = idx
break
# if None, add newInterval to the end
if start_idx == -1:
return intervals + [newInterval]
# - Add to the output all the intervals starting before newInterval
before_start = intervals[:start_idx]
# - Add all overlaping intervals to inserted_interval
inserted_interval = [
min(newInterval[0], intervals[start_idx][0]), newInterval[1]
]
idx = start_idx
while idx < len(intervals) and inserted_interval[1] >= intervals[idx][0]:
inserted_interval[1] = max(intervals[idx][1], inserted_interval[1])
idx += 1
return before_start + [inserted_interval] + intervals[idx:]
"""
"""
class Solution_:
def insert(self, intervals: List[List[int]], newInterval: List[int]):
# - Find the insert position (first interval with ending greater than newInterval's start)
start_idx = -1
for idx, interval in enumerate(intervals):
if interval[1] >= newInterval[0]:
start_idx = idx
break
# if None, add newInterval to the end
if start_idx == -1:
return intervals + [newInterval]
# - Add to the output all the intervals starting before newInterval
merged = intervals[:start_idx]
# - Add newInterval to output
if len(merged) > 0 and newInterval[0] <= merged[-1][1]:
merged[-1] = self.merge_intervals(newInterval, merged[-1])
else:
merged.append(newInterval)
# - Add to the output all the intervals starting after newInterval
for idx in range(start_idx, len(intervals)):
# Merge it with the last added interval if newInterval starts before the last added interval.
if intervals[idx][0] <= merged[-1][1]:
merged[-1] = self.merge_intervals(intervals[idx], merged[-1])
else:
merged.append(intervals[idx])
return merged
def merge_intervals(self, one, two):
return [min(one[0], two[0]), max(one[1], two[1])]
Container With Most Water
Best Time to Buy and Sell Stock
Best Time to Buy and Sell Stock
Best Time to Buy and Sell Stock II
Trapping Rain Water
-
Best Time to Buy and Sell Stock *
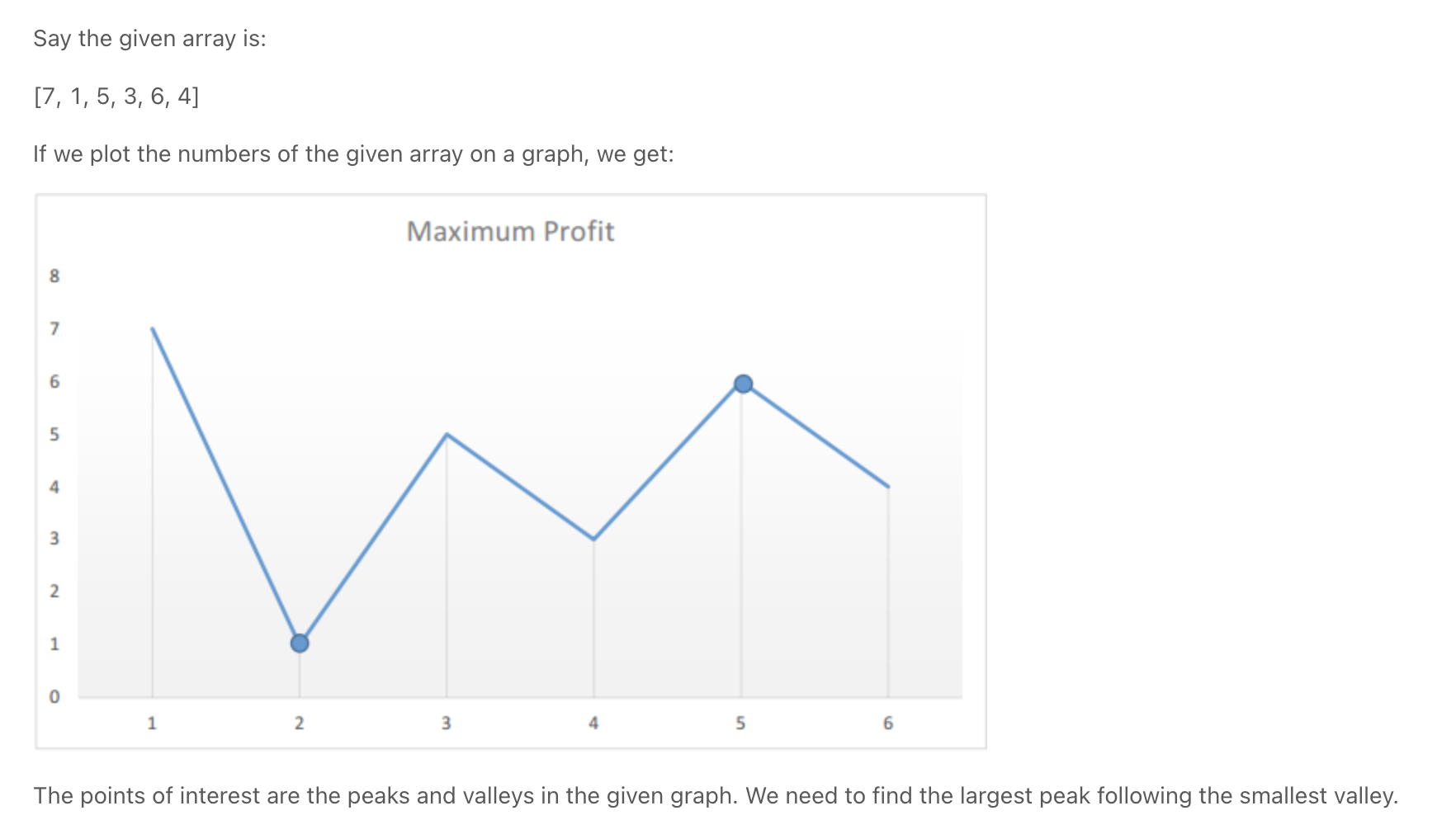
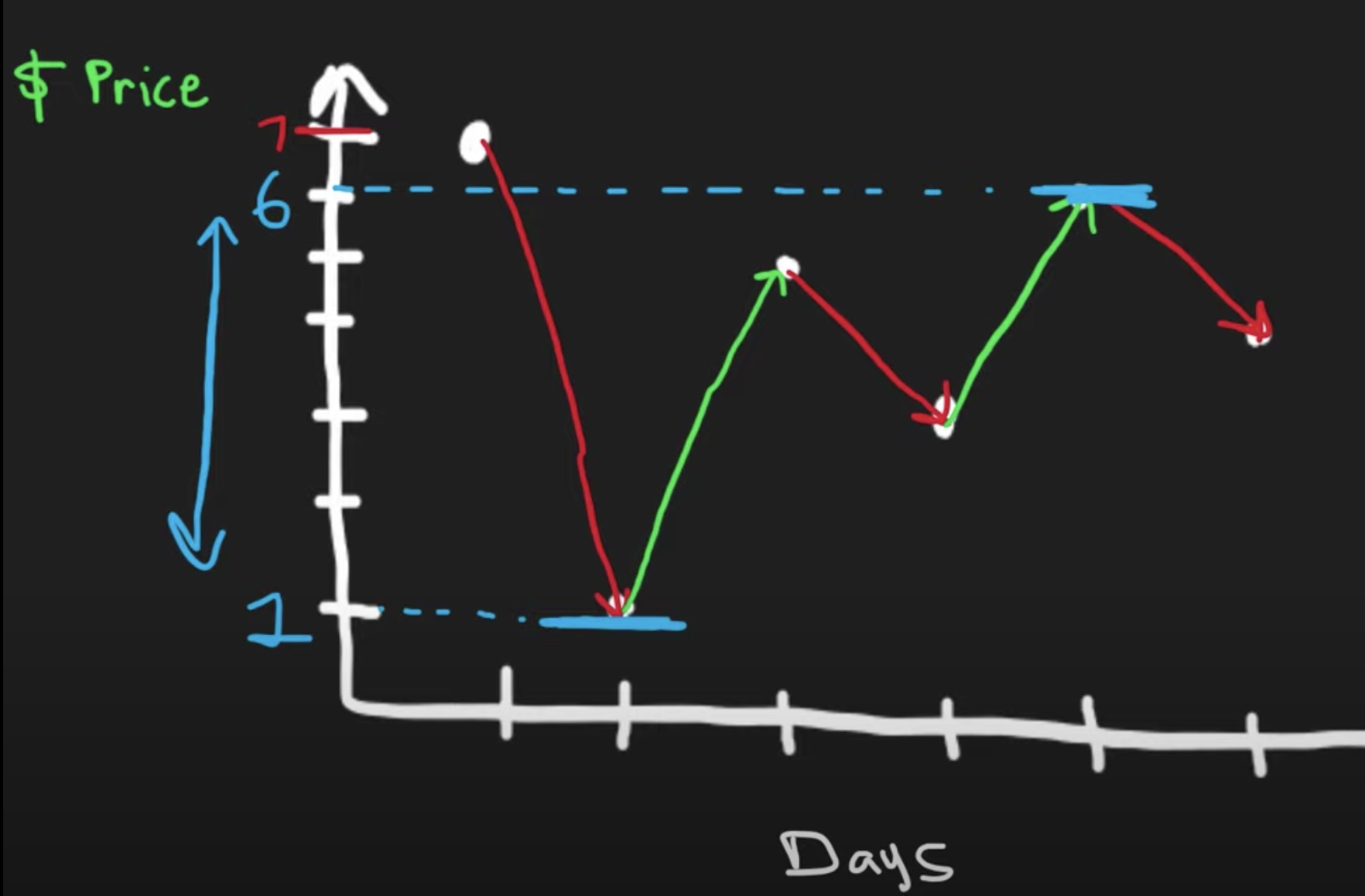
min & max gives maximum profit
""" Best Time to Buy and Sell Stock: (do Container With Most Water first) Say you have an array for which the ith element is the price of a given stock on day i. If you were only permitted to complete at most one transaction (i.e., buy one and sell one share of the stock), design an algorithm to find the maximum profit. Note that you cannot sell a stock before you buy one. Example 1: Input: [7,1,5,3,6,4] Output: 5 Explanation: Buy on day 2 (price = 1) and sell on day 5 (price = 6), profit = 6-1 = 5. Not 7-1 = 6, as selling price needs to be larger than buying price. Example 2: Input: [7,6,4,3,1] Output: 0 Explanation: In this case, no transaction is done, i.e. max profit = 0. https://leetcode.com/problems/best-time-to-buy-and-sell-stock/ """ class Solution_: def maxProfit(self, prices): min_price, max_profit = float('inf'), 0 for price in prices: profit = price - min_price max_profit = max(max_profit, profit) min_price = min(min_price, price) return max_profit class Solution: def maxProfit(self, prices): if len(prices) < 2: return 0 left = 0 right = 1 max_profit = 0 # we need to find the smallest valley following the largest peak -> try to continue increasing the slope while right < len(prices): max_profit = max(max_profit, prices[right] - prices[left]) # try out all values that are larger than left b4 we get a smaller value left # increase slope length if prices[right] > prices[left] or right == left: right += 1 # # if we find a point that is equal or lower than left (if lower **we might make more profit**) # reset slope else: left = right # move left to the smaller value right += 1 return max_profit -
Best Time to Buy and Sell Stock II

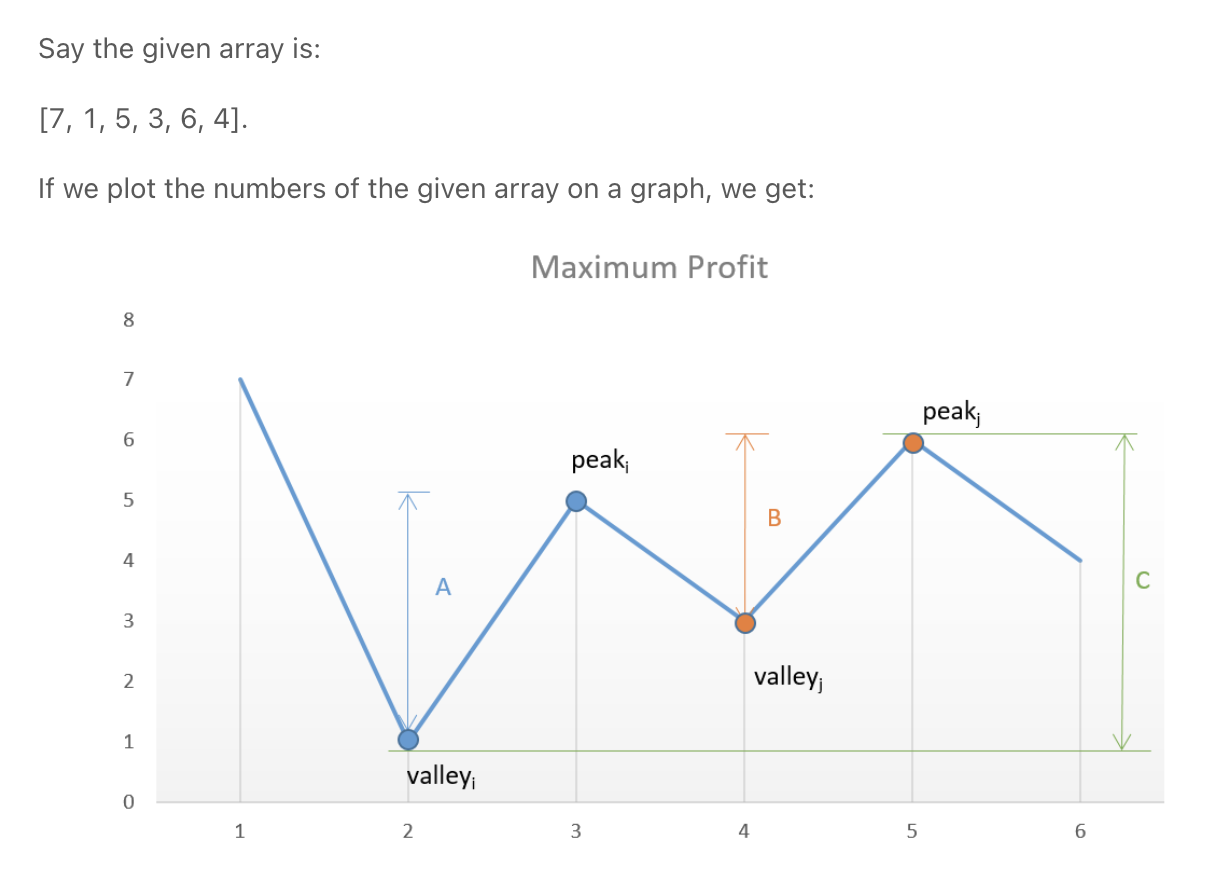
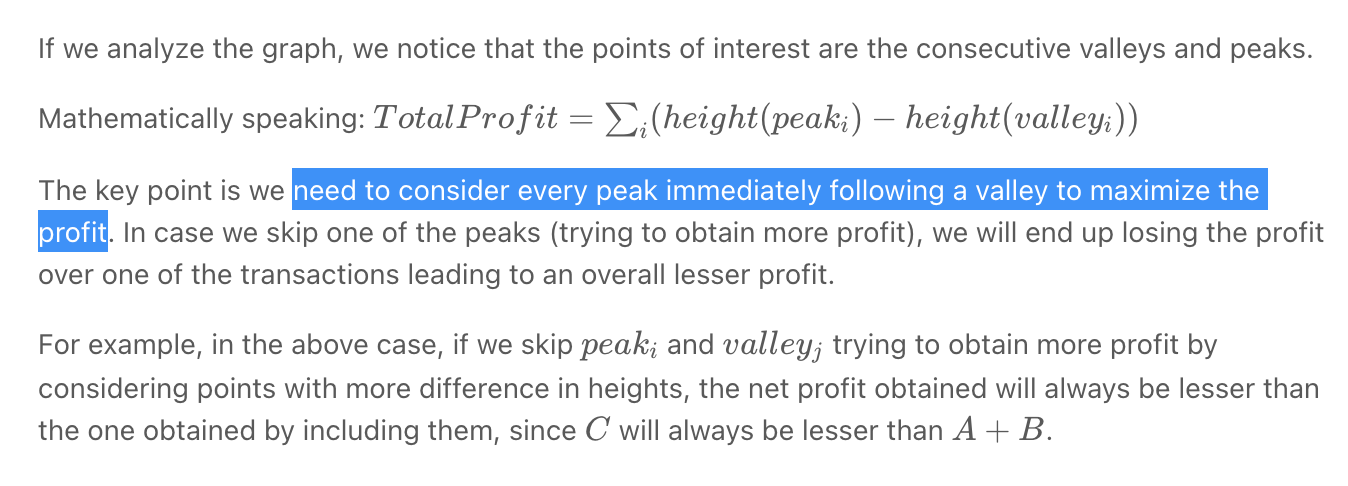
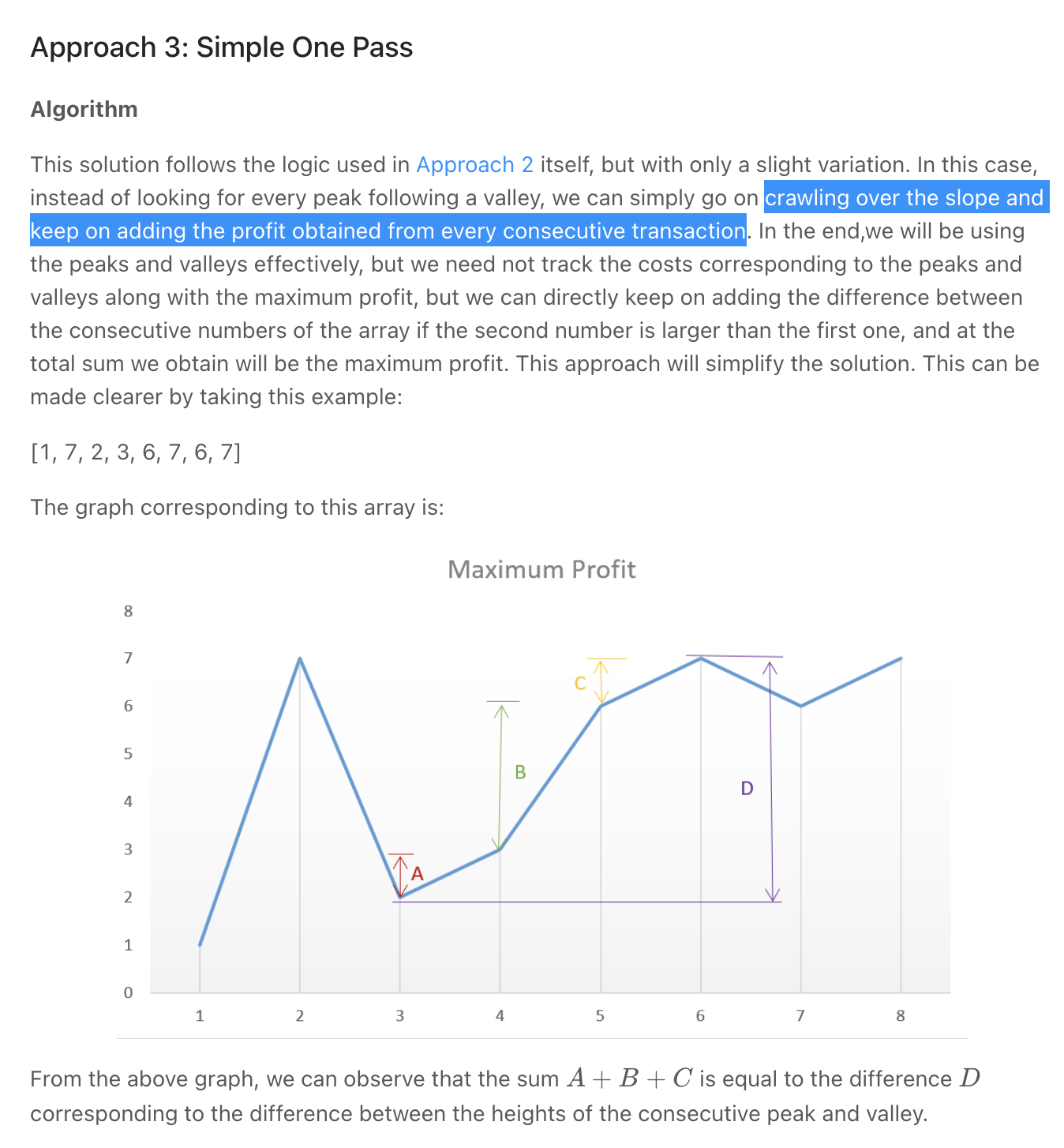
""" Best Time to Buy and Sell Stock II You are given an integer array prices where prices[i] is the price of a given stock on the ith day. On each day, you may decide to buy and/or sell the stock. You can only hold at most one share of the stock at any time. However, you can buy it then immediately sell it on the same day. Find and return the maximum profit you can achieve. Example 1: Input: prices = [7,1,5,3,6,4] Output: 7 Explanation: Buy on day 2 (price = 1) and sell on day 3 (price = 5), profit = 5-1 = 4. Then buy on day 4 (price = 3) and sell on day 5 (price = 6), profit = 6-3 = 3. Total profit is 4 + 3 = 7. Example 2: Input: prices = [1,2,3,4,5] Output: 4 Explanation: Buy on day 1 (price = 1) and sell on day 5 (price = 5), profit = 5-1 = 4. Total profit is 4. Example 3: Input: prices = [7,6,4,3,1] Output: 0 Explanation: There is no way to make a positive profit, so we never buy the stock to achieve the maximum profit of 0. https://leetcode.com/problems/best-time-to-buy-and-sell-stock-ii """ class Solution: def maxProfit(self, prices): """ If we analyze the graph, we notice that the points of interest are the consecutive valleys and peaks. Add every upward slope (valley->peak) https://www.notion.so/paulonteri/Two-Pointers-78c9f1659ca14bbbadace29a5d252a41#ca35efcb515445a091c0a0dfcefed057 """ result = 0 prev_min = prices[0] prev_max = prices[0] for idx in range(1, len(prices)): if prices[idx] < prev_max: # add prev slope we were on result += prev_max-prev_min # reset slope prev_max = prices[idx] prev_min = prices[idx] else: # increase slope prev_max = prices[idx] # add prev slope we were on result += prev_max-prev_min return result """ """ class Solution_: def maxProfit(self, prices): """ go on crawling over every slope and keep on adding the profit obtained from every consecutive transaction """ result = 0 for idx in range(1, len(prices)): if prices[idx] > prices[idx-1]: result += prices[idx] - prices[idx-1] return result -
Container With Most Water *
Trapping Rain Water (but not considering the water lost by the area/volume of bars)

Screen Recording 2021-09-21 at 18.50.42.mov

""" Container With Most Water: (do Best Time to Buy and Sell Stock next) Given n non-negative integers a1, a2, ..., an , where each represents a point at coordinate (i, ai). n vertical lines are drawn such that the two endpoints of the line i is at (i, ai) and (i, 0). Find two lines, which, together with the x-axis forms a container, such that the container contains the most water. Notice that you may not slant the container. https://leetcode.com/problems/container-with-most-water/ Trapping Rain Water (but not considering the water lost by the area/volume of bars) """ class SolutionBF: def maxArea(self, height): max_area = 0 for idx in range(len(height)): for idx_two in range(idx+1, len(height)): h = min(height[idx], height[idx_two]) w = idx_two - idx max_area = max(max_area, w*h) return max_area """ The intuition behind this approach is that the area formed between the lines will always be limited by the height of the shorter line. Further, the farther the lines, the more will be the area obtained. We take two pointers, one at the beginning and one at the end of the array constituting the length of the lines. Futher, we maintain a variable maxarea to store the maximum area obtained till now. At every step, we find out the area formed between them, update maxarea and move the pointer pointing to the shorter line towards the other end by one step. """ class Solution: def maxArea(self, height): max_area = 0 left, right = 0, len(height) - 1 while left < right: # calculate area h = min(height[left], height[right]) w = right - left max_area = max(max_area, h*w) # move pointer if height[left] > height[right]: right -= 1 else: left += 1 return max_area -
Trapping Rain Water *
Trapping Rain Water - Google Interview Question - Leetcode 42
Trapping Rainwater Problem | Leetcode #42
Container With Most Water (but considering the water lost by the area/volume of bars)
Screen Recording 2021-10-27 at 14.33.50.mov
""" Trapping Rain Water Given n non-negative integers representing an elevation map where the width of each bar is 1, compute how much water it can trap after raining. Example 1: Input: height = [0,1,0,2,1,0,1,3,2,1,2,1] Output: 6 Explanation: The above elevation map (black section) is represented by array [0,1,0,2,1,0,1,3,2,1,2,1]. In this case, 6 units of rain water (blue section) are being trapped. Example 2: Input: height = [4,2,0,3,2,5] Output: 9 https://leetcode.com/problems/trapping-rain-water Container With Most Water (but considering the water lost by the area/volume of bars) """ from typing import List """ 3 | 2 | | | | 1 | || | | | | | | 0 0,1,0,2,1,0,1,3,2,1,2,1 5 | 4 | | 3 | | | 2 | | | | | 1 | | | | | [4,2,0,3,2,5] """ # O(N) space | O(N) time class Solution: def trap(self, height: List[int]): """ - the water stored at a particular height is - min(max_left, max_right) - height # negatives are ignored - the max of the furthest ends are the furthest ends heights """ total_water = 0 # calculate max heights max_left = height[:] max_right = height[:] for idx in range(1, len(height)): max_left[idx] = max(height[idx], max_left[idx-1]) for idx in reversed(range(len(height)-1)): max_right[idx] = max(height[idx], max_right[idx+1]) # calculate water above for idx, curr_height in enumerate(height): water = min(max_left[idx], max_right[idx]) - curr_height if water > 0: total_water += water return total_water """ """ # O(1) space | O(N) time class Solution_: def trap(self, height: List[int]): """ - maintain max left & right on the go: - https://youtu.be/ZI2z5pq0TqA?t=663 - https://youtu.be/C8UjlJZsHBw?t=1413 - have a left and right pointer at each end of the array - if one pointer (small_pointer) has a value less than the other: * the water on small_pointer's next will be most affected by small_pointer as we consider min(max_left, max_height) * another way we can think about this is that we can try to increase the small_pointer's value - move that pointer forward - and record (where we have moved to)'s water """ total_water = 0 max_left, max_right = height[0], height[-1] left, right = 0, len(height)-1 while left < right: # # left smaller if height[left] < height[right]: max_left = max(height[left], max_left) # calculate water at next position - remember that we know that the water at the right is greater than this water_at_next = max_left - height[left+1] if water_at_next > 0: total_water += water_at_next # move forward left += 1 # # right smaller else: max_right = max(height[right], max_right) # calculate water at next position - remember that we know that the water at the right is equal to/greater than this water_at_next = max_right - height[right-1] if water_at_next > 0: total_water += water_at_next # move forward right -= 1 return total_water
Strobogrammatic Number II *
More examples
- Intervals Intersection
-
'K' Closest Numbers
-
Longest Substring with At Most K Distinct Characters
""" 340. Longest Substring with At Most K Distinct Characters: Given a string s and an integer k, return the length of the longest substring of s that contains at most k distinct characters. Example 1: Input: s = "eceba", k = 2 Output: 3 Explanation: The substring is "ece" with length 3. Example 2: Input: s = "aa", k = 1 Output: 2 Explanation: The substring is "aa" with length 2. https://leetcode.com/problems/longest-substring-with-at-most-k-distinct-characters """ import collections class Solution: def lengthOfLongestSubstringKDistinct(self, s: str, k: int): if len(s) <= 0 or k == 0: return 0 store = collections.defaultdict(int) idx = 0 while idx < len(s) and len(store) < k: store[s[idx]] += 1 idx += 1 longest = idx left = 0 for right in range(idx, len(s)): store[s[right]] += 1 while len(store) > k: store[s[left]] -= 1 if store[s[left]] == 0: store.pop(s[left]) left += 1 longest = max(longest, (right-left)+1) return longest
Find the original version of this page (with additional content) on Notion here.
Created: December 13, 2021 16:05:48