Cyclic Sort
Cyclic Sort - Explained - LeetCode Discuss
This pattern describes an interesting approach to deal with problems involving arrays containing numbers in a given range. For example, take the following problem:
You are given an unsorted array containing numbers taken from the range 1 to ‘n’. The array can have duplicates, which means that some numbers will be missing. Find all the missing numbers.
To efficiently solve this problem, we can use the fact that the input array contains numbers in the range of 1 to ‘n’. For example, to efficiently sort the array, we can try placing each number in its correct place, i.e., placing ‘1’ at index ‘0’, placing ‘2’ at index ‘1’, and so on. Once we are done with the sorting, we can iterate the array to find all indices that are missing the correct numbers. These will be our required numbers.
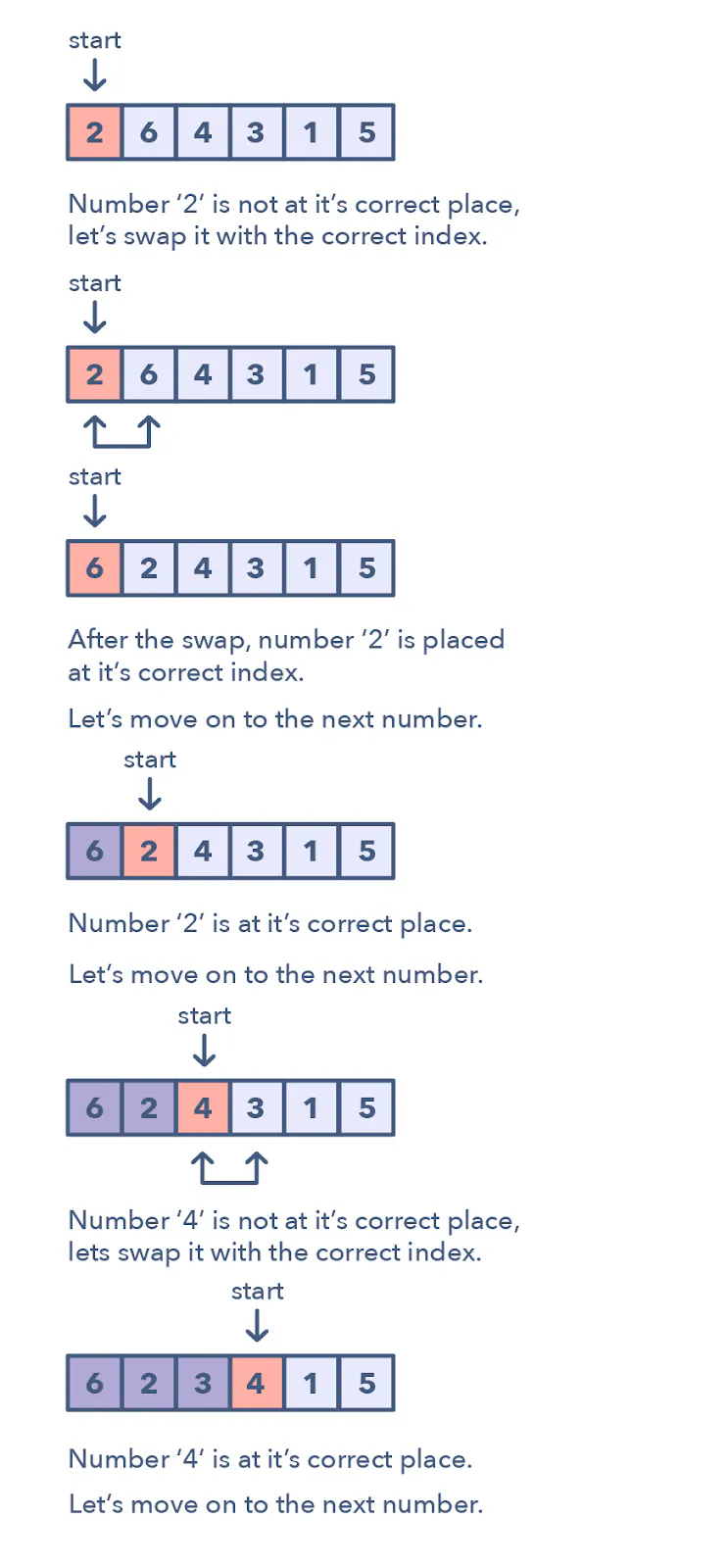
This pattern describes an interesting approach to deal with problems involving arrays containing numbers in a given range. The Cyclic Sort pattern iterates over the array one number at a time, and if the current number you are iterating is not at the correct index, you swap it with the number at its correct index.
How do I identify this pattern?
- They will be problems involving a sorted array with numbers in a given range
- If the problem asks you to find the missing/duplicate/smallest number in an sorted/rotated array
Cyclic Sort
"""
Cyclic Sort:
We are given an array containing ‘n’ objects.
Each object, when created, was assigned a unique number from 1 to ‘n’ based on their creation sequence.
This means that the object with sequence number ‘3’ was created just before the object with sequence number ‘4’.
Write a function to sort the objects in-place on their creation sequence number in O(n) and without any extra space.
For simplicity, let’s assume we are passed an integer array containing only the sequence numbers, though each number is actually an object.
There are no duplicates
Example 1:
Input: [3, 1, 5, 4, 2]
Output: [1, 2, 3, 4, 5]
Example 2:
Input: [2, 6, 4, 3, 1, 5]
Output: [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6]
Example 3:
Input: [1, 5, 6, 4, 3, 2]
Output: [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6]
"""
"""
As we know, the input array contains numbers in the range of 1 to ‘n’. We can use this fact to devise an efficient way to sort the numbers.
Since all numbers are unique, we can try placing each number at its correct place, i.e., placing ‘1’ at index ‘0’, placing ‘2’ at index ‘1’, and so on.
"""
def cyclic_sort(nums):
idx = 0
while idx < len(nums):
if nums[idx] != idx+1:
# nums[num-1], nums[idx] = nums[idx], nums[num-1]
nums[nums[idx]-1], nums[idx] = nums[idx], nums[nums[idx]-1]
continue
idx += 1
return nums
Find the Missing Number
"""
Find the Missing Number:
We are given an array containing ‘n’ distinct numbers taken from the range 0 to ‘n’.
Since the array has only ‘n’ numbers out of the total ‘n+1’ numbers, find the missing number.
Example 1:
Input: [4, 0, 3, 1]
Output: 2
Example 2:
Input: [8, 3, 5, 2, 4, 6, 0, 1]
Output: 7
"""
"""
Since the input array contains unique numbers from the range 0 to ‘n’,
we can use a similar strategy as discussed in Cyclic Sort to place the numbers on their correct index.
Once we have every number in its correct place,
we can iterate the array to find the index which does not have the correct number, and that index will be our missing number.
"""
def find_missing_number(nums):
idx = 0
while idx < len(nums):
num_in_range = nums[idx] >= 0 and nums[idx] < len(nums)
if num_in_range and nums[idx] != idx:
# nums[num-1], nums[idx] = nums[idx], nums[num-1]
nums[nums[idx]], nums[idx] = nums[idx], nums[nums[idx]]
continue
idx += 1
for idx in range(len(nums)):
if nums[idx] != idx:
return idx
return -1
First Missing Positive
https://leetcode.com/problems/first-missing-positive/
Find All Numbers Disappeared in an Array
"""
Find All Numbers Disappeared in an Array:
Given an array nums of n integers where nums[i] is in the range [1, n],
return an array of all the integers in the range [1, n] that do not appear in nums.
Example 1:
Input: nums = [4,3,2,7,8,2,3,1]
Output: [5,6]
Example 2:
Input: nums = [1,1]
Output: [2]
Constraints:
n == nums.length
1 <= n <= 105
1 <= nums[i] <= n
Could you do it without extra space and in O(n) runtime? You may assume the returned list does not count as extra space.
"""
class Solution:
def findDisappearedNumbers(self, nums):
result = []
idx = 0
while idx < len(nums):
num = nums[idx]
if num-1 != idx and nums[num-1] != num:
nums[num-1], nums[idx] = nums[idx], nums[num-1]
continue
idx += 1
for idx in range(len(nums)):
if nums[idx]-1 != idx:
result.append(idx+1)
return result
Find the original version of this page (with additional content) on Notion here.
Created: December 13, 2021 16:05:48